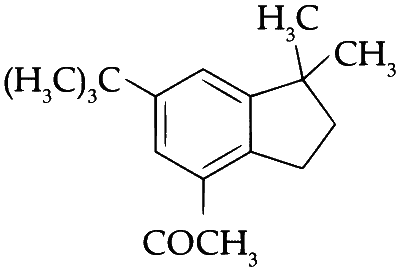
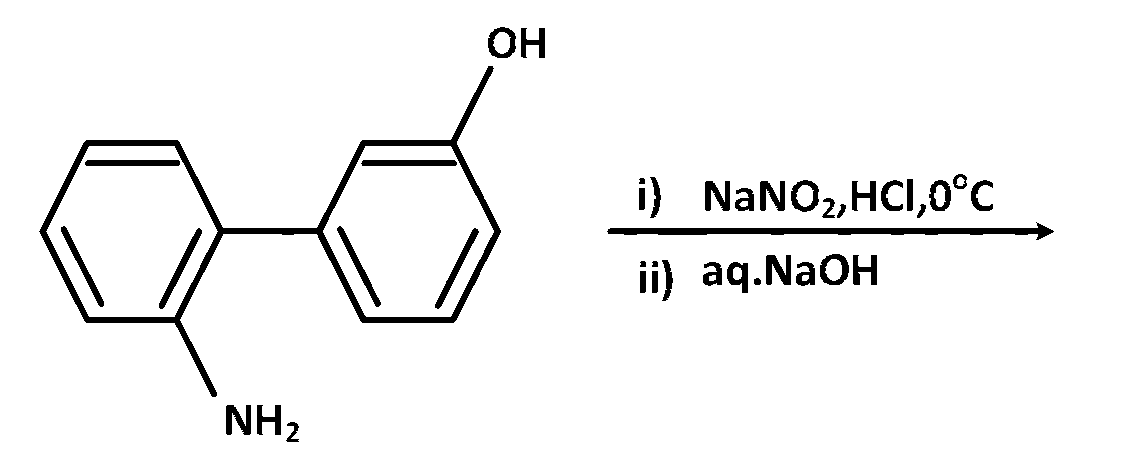
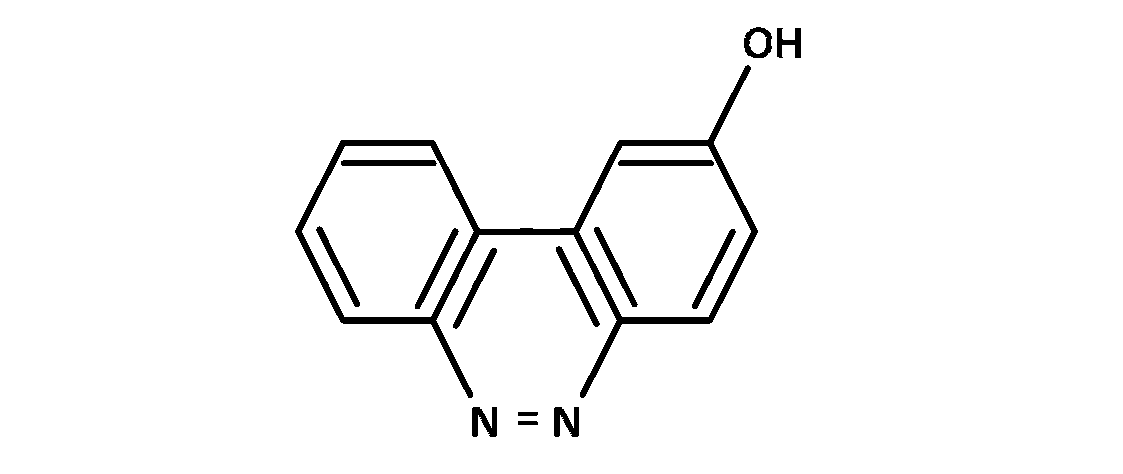
JEE Advance - Chemistry (2017 - Paper 2 Offline)
1
Pure water freezes at $$273$$ $$K$$ and $$1$$ bar. The addition of $$34.5$$ $$g$$ of ethanol to $$500$$ $$g$$ of water changes the freezing point of the solution. Use the freezing point depression constant of water as $$2$$ kg $$mo{l^{ - 1}}.$$ The figures shown below represent plots of vapor pressure $$(V.P.)$$ versus temperature $$(T).$$ [molecular weight of ethanol is $$46$$ $$g$$ $$mo{l^{ - 1}}.$$ ] Among the following, the option representing change in the freezing point is
Answer
(C)

5
Compounds $$P$$ and $$R$$ upon ozonolysis produce $$Q$$ and $$S,$$ respectively. The molecular formula of $$Q$$ and $$S$$ is $${C_8}{H_8}O.Q$$ undergoes Canninzzaro reaction but not haloform reaction, whereas $$S$$ undergoes haloform reaction but not Cannizzaro reaction
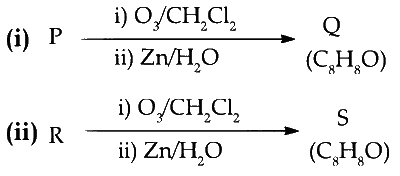
The option(s) with suitable combination of $$P$$ and $$R,$$ respectively, is (are)
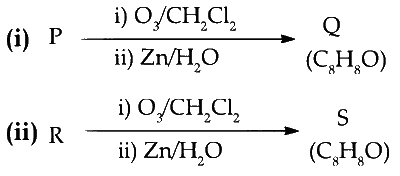
The option(s) with suitable combination of $$P$$ and $$R,$$ respectively, is (are)
Answer
A
B
16
The standard state Gibbs free energies of formation of $$C$$(graphite) and $$C$$(diamond) at $$T=298$$ $$K$$ are
$${\Delta _f}{G^0}$$ [$$C$$(graphite)] $$ = 0kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$$
$${\Delta _f}{G^0}$$ [$$C$$(diamond)] $$ = 2.9kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$$
The standard state means that the pressure should be $$1$$ bar, and substance should be pure at a given temperature. The conversion of graphite [$$C$$(graphite)] to diamond [$$C$$(diamond)] reduces its volume by $$2 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{m^3}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$ If $$C$$(graphite) is converted to $$C$$(diamond) isothermally at $$T=298$$ $$K,$$ the pressure at which $$C$$(graphite) is in equilibrium with $$C$$(diamond), is
[Useful information : $$1$$ $$J=1$$ $$kg\,{m^2}{s^{ - 2}};1\,Pa = 1\,kg\,{m^{ - 1}}{s^{ - 2}};$$ $$1$$ bar $$ = {10^5}$$ $$Pa$$]
$${\Delta _f}{G^0}$$ [$$C$$(graphite)] $$ = 0kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$$
$${\Delta _f}{G^0}$$ [$$C$$(diamond)] $$ = 2.9kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$$
The standard state means that the pressure should be $$1$$ bar, and substance should be pure at a given temperature. The conversion of graphite [$$C$$(graphite)] to diamond [$$C$$(diamond)] reduces its volume by $$2 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{m^3}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$ If $$C$$(graphite) is converted to $$C$$(diamond) isothermally at $$T=298$$ $$K,$$ the pressure at which $$C$$(graphite) is in equilibrium with $$C$$(diamond), is
[Useful information : $$1$$ $$J=1$$ $$kg\,{m^2}{s^{ - 2}};1\,Pa = 1\,kg\,{m^{ - 1}}{s^{ - 2}};$$ $$1$$ bar $$ = {10^5}$$ $$Pa$$]
Answer
(A)
$$14501$$ bar
17
For the following cell,
$$Zn\left( s \right)\left| {ZnS{O_4}\left( {aq} \right)} \right|\left| {CuS{O_4}\left( {aq} \right)} \right|Cu\left( s \right)$$
when the concentration of $$Z{n^{2 + }}$$ is $$10$$ times the concentration of $$C{u^{2 + }},$$ the expression for $$\Delta G$$ (in $$J\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$) is [$$F$$ is Faraday constant; $$R$$ is gas constant; $$T$$ is temperature; $${E^0}$$ (cell)$$=1.1$$ $$V$$]
$$Zn\left( s \right)\left| {ZnS{O_4}\left( {aq} \right)} \right|\left| {CuS{O_4}\left( {aq} \right)} \right|Cu\left( s \right)$$
when the concentration of $$Z{n^{2 + }}$$ is $$10$$ times the concentration of $$C{u^{2 + }},$$ the expression for $$\Delta G$$ (in $$J\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$) is [$$F$$ is Faraday constant; $$R$$ is gas constant; $$T$$ is temperature; $${E^0}$$ (cell)$$=1.1$$ $$V$$]
Answer
(B)
$$2.303RT-2.2F$$
18
The standard state Gibbs free energies of formation of $$C$$(graphite) and $$C$$(diamond) at $$T=298$$ $$K$$ are
$${\Delta _f}{G^0}$$ [$$C$$(graphite)] $$ = 0kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$$
$${\Delta _f}{G^0}$$ [$$C$$(diamond)] $$ = 2.9kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$$
The standard state means that the pressure should be $$1$$ bar, and substance should be pure at a given temperature. The conversion of graphite [$$C$$(graphite)] to diamond [$$C$$(diamond)] reduces its volume by $$2 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{m^3}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$ If $$C$$(graphite) is converted to $$C$$(diamond) isothermally at $$T=298$$ $$K,$$ the pressure at which $$C$$(graphite) is in equilibrium with $$C$$(diamond), is
[Useful information : $$1$$ $$J=1$$ $$kg\,{m^2}{s^{ - 2}};1\,Pa = 1\,kg\,{m^{ - 1}}{s^{ - 2}};$$ $$1$$ bar $$ = {10^5}$$ $$Pa$$]
$${\Delta _f}{G^0}$$ [$$C$$(graphite)] $$ = 0kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$$
$${\Delta _f}{G^0}$$ [$$C$$(diamond)] $$ = 2.9kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$$
The standard state means that the pressure should be $$1$$ bar, and substance should be pure at a given temperature. The conversion of graphite [$$C$$(graphite)] to diamond [$$C$$(diamond)] reduces its volume by $$2 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,{m^3}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$ If $$C$$(graphite) is converted to $$C$$(diamond) isothermally at $$T=298$$ $$K,$$ the pressure at which $$C$$(graphite) is in equilibrium with $$C$$(diamond), is
[Useful information : $$1$$ $$J=1$$ $$kg\,{m^2}{s^{ - 2}};1\,Pa = 1\,kg\,{m^{ - 1}}{s^{ - 2}};$$ $$1$$ bar $$ = {10^5}$$ $$Pa$$]
Answer
(A)
$$14501$$ bar