JEE Advance - Physics (2007 - Paper 2 Offline)
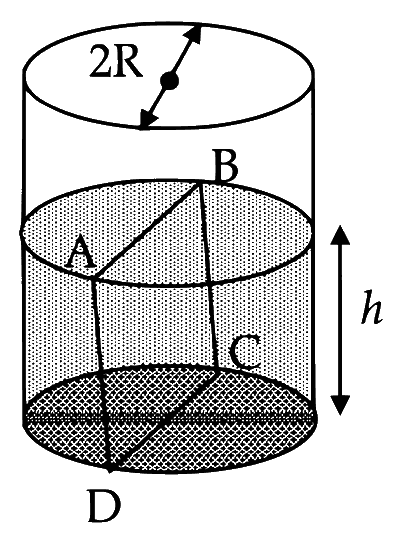
Water is filled up to a height $$h$$ in a beaker of radius $$R$$ as shown in the figure. The density of water is $$\rho$$, the surface tension of water is $$T$$ and the atmospheric pressure is P. Consider a vertical section $$A B C D$$ of the water column through a diameter of the beaker. The force on water on one side of this section by water on the other side of this section has magnitude
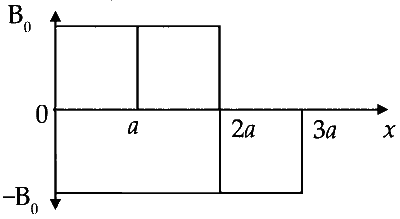
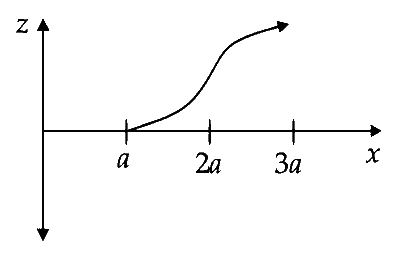
A magnetic field $$\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}=\mathrm{B}_{0} \hat{j}$$ exists in the region $$a < x < 2 a$$ and $$\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}=-\mathrm{B}_{0} \hat{j}$$, in the region $$2 a < x < 3 a$$, where $$\mathrm{B}_{0}$$ is a positive constant. A positive point charge moving with a velocity $$\vec{v}=v_{0} \hat{i}$$, where $$v_{0}$$ is a positive constant, enters the magnetic field at $$x=a$$. The trajectory of the charge in this region can be like,
STATEMENT 1
A cloth covers a table. Some dishes are kept on it. The cloth can be pulled out without dislodging the dishes from the table.
Because
STATEMENT 2
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
STATEMENT 1
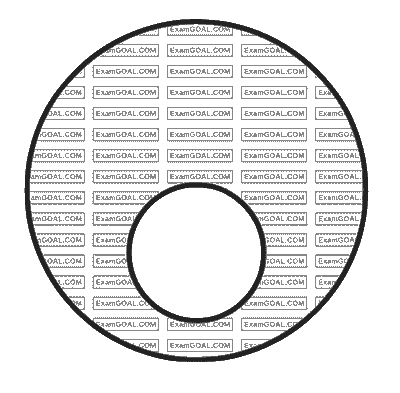
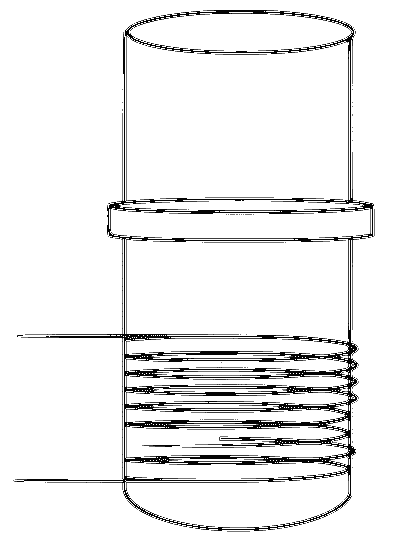
A vertical iron rod has a coil of wire wound over it at the bottom end. An alternating current flows in the coil. The rod goes through a conducting ring as shown in the figure. The ring can float at a certain height above the coil.
Because
STATEMENT 2
In the above situation, a current is induced in the ring which interacts with the horizontal component of the magnetic field to produce an average force in the upward direction.
STATEMENT 1
The total translational kinetic energy of all the molecules of a given mass of an ideal gas is 1.5 times the product of its pressure and its volume.
Because
STATEMENT 2
The molecules of a gas collide with each other and the velocities of the molecules change due to the collision.
Column I describe some situations in which a small object moves. Column II describes some characteristics of these motions. Match the situation in Column I with the characteristics in Column II and indicate your answer by darkening appropriate bubbles in the $$4 \times 4$$ matrix given in the ORS.
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | The object moves on the x-axis under a conservative force in such a way that its "speed" and "position" satisfy $$v = {c_1}\sqrt {{c_2} - {x^2}} $$, where $$c_1$$ and $$c_2$$ are positive constants. | (P) | The object executes a simple harmonic motion. |
| (B) | The object moves on the x-axis in such a way that its velocity and its displacement from the origin satisfy $$v=-kx$$, where $$k$$ is a positive constant. | (Q) | The object does not change its direction. |
| (C) | The object is attached to one end of a massless spring of a given spring constant. The other end of the spring is attached to the ceiling of an elevator. Initially everything is at rest. The elevator starts going upwards with a constant acceleration a. The motion of the object is observed from the elevator during the period it maintains this acceleration. | (R) | The kinetic energy of the object keeps on decreasing |
| (D) | The object is projected from the earth's surface vertically upwards with a speed $$2\sqrt {GMe/{\mathop{\rm Re}\nolimits} } $$, where, M$$_e$$ is the mass of the earth and R$$_e$$ is the radius of the earth. Neglect forces from objects other than the earth. | (S) | The object can change its direction only once. |
Two wires each carrying a steady current I are shown in four configurations in Column I. Some of the resulting effects are described in Column II. Match the statements in Column I with the statements in Column II and indicate your answer by darkening appropriate bubbles in the $$4 \times 4$$ matrix given in the ORS.
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | Point P is situated midway between the wires.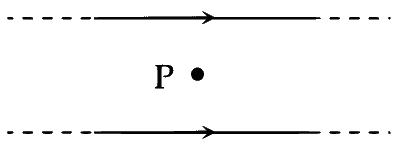 |
(P) | The magnetic fields (B) at P due to the currents in the wire are in same direction. |
| (B) | Point P is situated at the mid-point of the line joining the centers of the circular wires, which have same radii.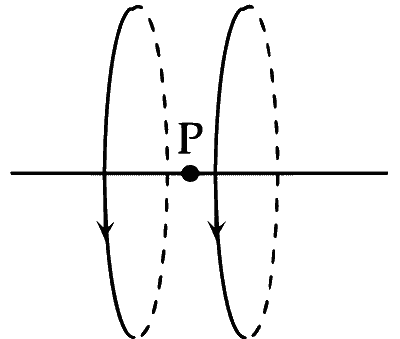 |
(Q) | The magnetic fields (B) at P due to the currents in the wires are in opposite directions. |
| (C) | Point P is situated at the mid-point of the line joining the centers of the circular wires, which have same radii.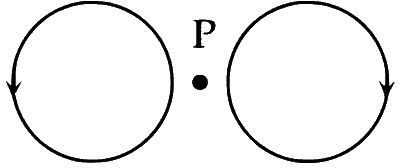 |
(R) | There is no magnetic field at P. |
| (D) | Point P is situated at the common center of the wires.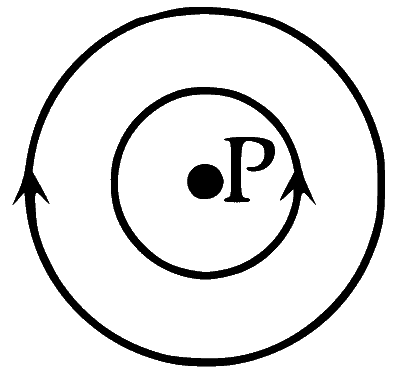 |
(S) | The wires repel each other. |
Column I gives some devices and Column II gives some process on which the functioning of these devices depend. Match the devices in Column I with the processes in Column II and indicate your answer by darkening appropriate bubbles in the $$4 \times 4$$ matrix given in the ORS.
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | Bimetallic strip | (P) | Radiation from a hot body |
| (B) | Steam engine | (Q) | Energy conversion |
| (C) | Incandescent lamp | (R) | Melting |
| (D) | Electric fuse | (S) | Thermal expansion |