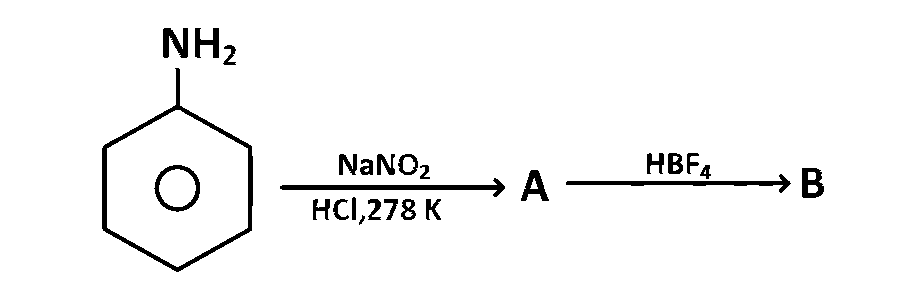
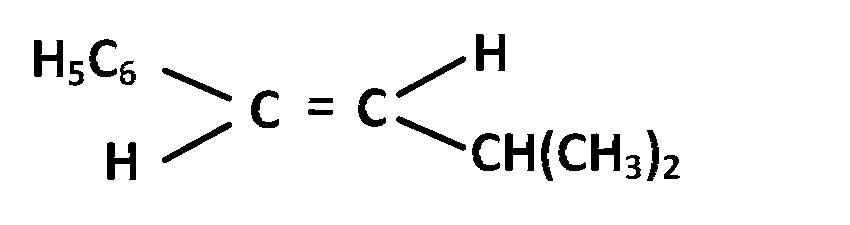
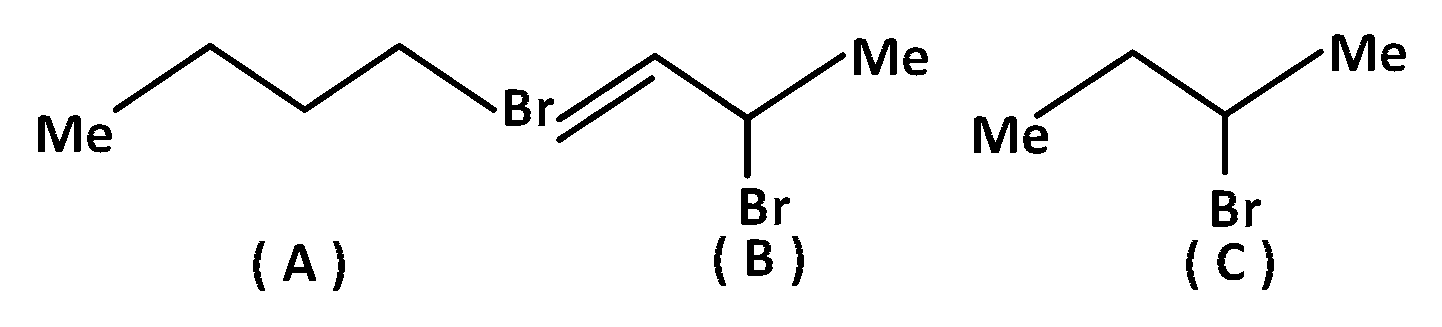
JEE MAIN - Chemistry (2010)
15
A solution containing 2.675g of CoCl3. 6NH3 (molar mass = 267.5 g mol–1) is passed through a cation exchanger. The chloride ions obtained in solution were treated with excess of AgNO3 to give
4.78 g of AgCl (molar mass = 143.5 g mol–1). The formula of the complex is : (At. Mass of Ag = 108 u)
Answer
(A)
[Co(NH3)6]Cl3
17
29.5 mg of an organic compound containing nitrogen was digested according to Kjeldahl’s method
and the evolved ammonia was absorbed in 20 mL of 0.1 M HCl solution. The excess of the acid
required 15 mL of 0.1 M NaOH solution for complete neutralization. The percentage of nitrogen in
the compound is
Answer
(C)
23.7
19
Consider the reaction :
Cl2(aq) + H2S(aq) → S(s) + 2H+ (aq) + 2Cl– (aq)
The rate equation for this reaction is rate = k [Cl2] [H2S]
Which of these mechanisms is/are consistent with this rate equation?
(A) Cl2 + H2S $$\to$$ H+ + Cl– + Cl+ + HS– (slow)
Cl+ + HS– $$\to$$ H+ + Cl– + S (fast)
(B) H2S $$ \Leftrightarrow $$ H+ + HS– (fast equilibrium)
Cl2 + HS– $$\to$$ 2Cl– + H+ + S (slow)
Answer
(D)
A only
22
On mixing, heptane and octane form an ideal solution. At 373 K, the vapour pressures of the two
liquid components (heptane and octane) are 105 kPa and 45 kPa respectively. Vapour pressure of
the solution obtained by mixing 25.0g of heptane and 35 g of octane will be (molar mass of heptane = 100 g mol–1 and of octane = 114 g mol–1)
Answer
(A)
72.0 kPa