JEE Advance - Physics (2025 - Paper 2 Online - No. 7)
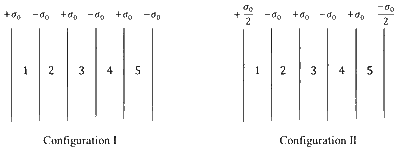
Six infinitely large and thin non-conducting sheets are fixed in configurations I and II. As shown in the figure, the sheets carry uniform surface charge densities which are indicated in terms of $\sigma_0$. The separation between any two consecutive sheets is $1~\mu \text{m}$. The various regions between the sheets are denoted as 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. If $\sigma_0 = 9~\mu\text{C/m}^2$, then which of the following statements is/are correct:
(Take permittivity of free space $\epsilon_0 = 9 \times 10^{-12}$ F/m)
Explanation
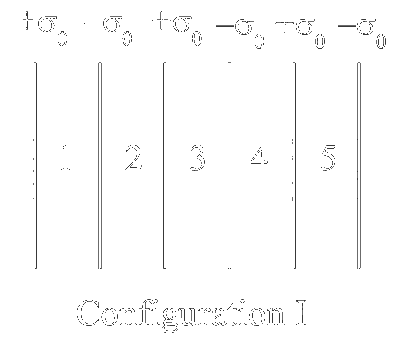
$\begin{aligned}\left(E_4\right)_I= & \frac{\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0}[1-1+1-1-1+1]=0 \\ \left(V_{\text {First }}\right)_I & =\frac{-\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0}[-1+2-3+4-5] \mathrm{d} \\ & =\frac{-\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0}[-3] \mathrm{d}=\frac{\sigma_0 3 \mathrm{~d}}{2 \epsilon_0}\end{aligned}$
$\begin{aligned} & \begin{aligned}\left(V_{\text {Last }}\right)_I & =\frac{-\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0}[1-2+3-4+5] \\ & =\frac{\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0}[-3 \mathrm{~d}]\end{aligned} \\ & \begin{aligned}\left(V_{\text {First }}-V_{\text {Last }}\right)_I & =\frac{3 \sigma_0 \mathrm{~d}}{\epsilon_0} \\ & =\frac{3 \times 9 \times 10^{-6} \times 1 \times 10^{-6}}{9 \times 10^{-12}}=3 \mathrm{volt}\end{aligned}\end{aligned}$
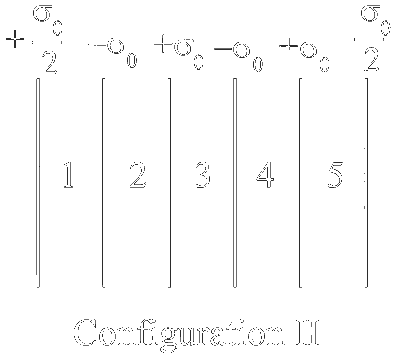 $\begin{aligned} & \begin{aligned}\left(\mathrm{E}_3\right)_{\text {II }}= & \frac{\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0}\left[\frac{1}{2}-1+1+1-1+\frac{1}{2}\right]=\frac{\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0} \\ & =\frac{-\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0}\left[-1+2-3+4-\frac{5}{2}\right] \mathrm{d} \\ & =\frac{-\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0}[2-2.5] \mathrm{d}=\frac{\sigma_0 \mathrm{~d}}{4 \epsilon_0}\end{aligned} \\ & \left(\mathrm{~V}_{\text {Last }}\right)_{\text {II }}=\frac{-\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0}\left[1-2+3-4+\frac{5}{2}\right] \mathrm{d} \\ & \\ & \quad=\frac{-\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0}[6.5-6] \mathrm{d}=\frac{-\sigma_0 \mathrm{~d}}{4 \epsilon_0} \\ & \left(\mathrm{~V}_{\text {First }}-\mathrm{V}_{\text {Last }}\right)_{\text {II }}=\frac{\sigma_0 \mathrm{~d}}{2 \epsilon_0} \neq 0\end{aligned}$
$\begin{aligned} & \begin{aligned}\left(\mathrm{E}_3\right)_{\text {II }}= & \frac{\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0}\left[\frac{1}{2}-1+1+1-1+\frac{1}{2}\right]=\frac{\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0} \\ & =\frac{-\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0}\left[-1+2-3+4-\frac{5}{2}\right] \mathrm{d} \\ & =\frac{-\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0}[2-2.5] \mathrm{d}=\frac{\sigma_0 \mathrm{~d}}{4 \epsilon_0}\end{aligned} \\ & \left(\mathrm{~V}_{\text {Last }}\right)_{\text {II }}=\frac{-\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0}\left[1-2+3-4+\frac{5}{2}\right] \mathrm{d} \\ & \\ & \quad=\frac{-\sigma_0}{2 \epsilon_0}[6.5-6] \mathrm{d}=\frac{-\sigma_0 \mathrm{~d}}{4 \epsilon_0} \\ & \left(\mathrm{~V}_{\text {First }}-\mathrm{V}_{\text {Last }}\right)_{\text {II }}=\frac{\sigma_0 \mathrm{~d}}{2 \epsilon_0} \neq 0\end{aligned}$Comments (0)


