JEE Advance - Physics (2023 - Paper 2 Online - No. 16)
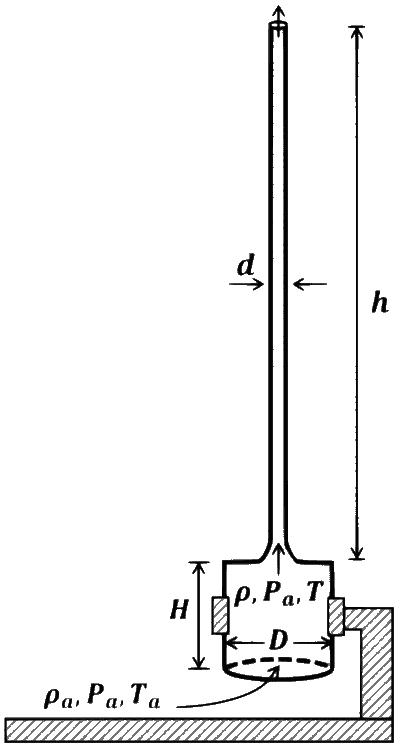
Considering the air flow to be streamline, the steady mass flow rate of air exiting the chimney is _________ $\mathrm{gm} \mathrm{s}^{-1}$.
Answer
47.1
Explanation
We know, $$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{P_a}=\frac{\rho R \mathrm{T}}{M}
\end{aligned}
$$
For a gas R and M are constant. So, $$\rho T$$ = Constant (for constant pressure).
The density of hot air inside the furnace is = $$\rho $$
The air gets heated inside the furnace at constant pressure Pa.
$$ \therefore $$ $$ \rho_{\mathrm{a}} \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{a}}=\rho \mathrm{T} $$
$$ \Rightarrow $$ 1.2 $$ \times $$ 300 = $$\rho $$ $$ \times $$ 360
$$\Rightarrow \rho=1 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^3$$
Buoyant force applied on the hot air = $\rho_{\mathrm{a}}$Vg (Upward direction)
Weight of the hot air = $$\rho $$Vg (Downward direction)
$$ \therefore $$ Net force on the hot air = $\rho_{\mathrm{a}}$Vg - $$\rho $$Vg
Let acceleration of the hot air in the upward direction = $a$
and mass of the hot air = $$\rho $$V
$$ \therefore $$ $$\rho $$V$a$ = $\rho_{\mathrm{a}}$Vg - $$\rho $$Vg
$$ \Rightarrow $$ $a$ = $${{{\rho _a}Vg - \rho Vg} \over {\rho V}}$$
= $${{{\rho _a}g - \rho g} \over \rho }$$
= $${{1.2 \times 10 - 1 \times 10} \over 1}$$
= 2 m/s2
$$ \therefore $$ Velocity(v) of the hot air when exiting the chimney using formula $${v^2} = {u^2} + 2ah$$,
$${v^2} = 0 + 2 \times 2 \times 9$$
$$ \Rightarrow $$ v = 6 m/s
Mass flow rate = $${{dm} \over {dt}}$$ = $$\rho $$Av
= $$ \rho \times \frac{\pi \mathrm{d}^2}{4} \times\mathrm{v}=1 \times \frac{\pi}{4} \times 10^{-2} \times 6 $$
= $${{471} \over {10000}}$$ kg/s = $${{471} \over {10000}} \times 1000$$ gm/s = 47.1
For a gas R and M are constant. So, $$\rho T$$ = Constant (for constant pressure).
The density of hot air inside the furnace is = $$\rho $$
The air gets heated inside the furnace at constant pressure Pa.
$$ \therefore $$ $$ \rho_{\mathrm{a}} \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{a}}=\rho \mathrm{T} $$
$$ \Rightarrow $$ 1.2 $$ \times $$ 300 = $$\rho $$ $$ \times $$ 360
$$\Rightarrow \rho=1 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^3$$
Buoyant force applied on the hot air = $\rho_{\mathrm{a}}$Vg (Upward direction)
Weight of the hot air = $$\rho $$Vg (Downward direction)
$$ \therefore $$ Net force on the hot air = $\rho_{\mathrm{a}}$Vg - $$\rho $$Vg
Let acceleration of the hot air in the upward direction = $a$
and mass of the hot air = $$\rho $$V
$$ \therefore $$ $$\rho $$V$a$ = $\rho_{\mathrm{a}}$Vg - $$\rho $$Vg
$$ \Rightarrow $$ $a$ = $${{{\rho _a}Vg - \rho Vg} \over {\rho V}}$$
= $${{{\rho _a}g - \rho g} \over \rho }$$
= $${{1.2 \times 10 - 1 \times 10} \over 1}$$
= 2 m/s2
$$ \therefore $$ Velocity(v) of the hot air when exiting the chimney using formula $${v^2} = {u^2} + 2ah$$,
$${v^2} = 0 + 2 \times 2 \times 9$$
$$ \Rightarrow $$ v = 6 m/s
Mass flow rate = $${{dm} \over {dt}}$$ = $$\rho $$Av
= $$ \rho \times \frac{\pi \mathrm{d}^2}{4} \times\mathrm{v}=1 \times \frac{\pi}{4} \times 10^{-2} \times 6 $$
= $${{471} \over {10000}}$$ kg/s = $${{471} \over {10000}} \times 1000$$ gm/s = 47.1
Comments (0)