JEE Advance - Physics (2023 - Paper 1 Online - No. 6)
Explanation
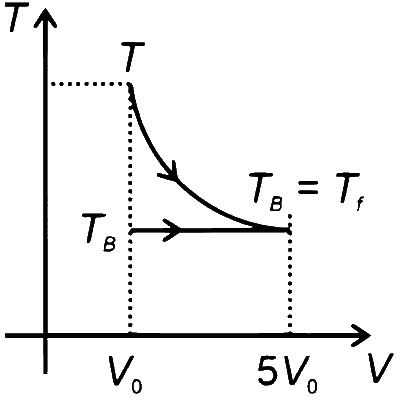
The expansion of an ideal gas can be analyzed using the thermodynamic relations for adiabatic and isothermal processes.
Adiabatic Expansion: For an adiabatic process, we use the relation involving temperatures and volumes at the initial and final states, which is given by :
$ TV^{\gamma-1} = \text{constant} $
Therefore, for the adiabatic expansion from $(T_A, V_0)$ to $(T_f, 5V_0)$, we have :
$ T_A V_0^{\gamma-1} = T_f (5V_0)^{\gamma-1} $
Simplifying, we get : $ T_A = T_f \times 5^{\gamma-1} $Isothermal Expansion : In an isothermal process, the temperature remains constant. So, $ T_B = T_f $ for the isothermal expansion from $(T_B, V_0)$ to $(T_f, 5V_0)$.
To find the ratio $ T_A / T_B $, we substitute the expressions for $ T_A $ and $ T_B $ :
$ \frac{T_A}{T_B} = \frac{T_f \times 5^{\gamma-1}}{T_f} $
$ \frac{T_A}{T_B} = 5^{\gamma-1} $
Therefore, the ratio $ T_A / T_B $ is $ 5^{\gamma-1} $, which corresponds to Option A.
Comments (0)


