JEE Advance - Physics (2022 - Paper 2 Online - No. 3)
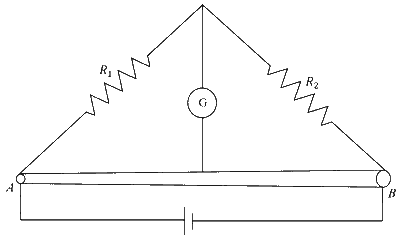
Two resistances $R_{1}=X \Omega$ and $R_{2}=1 \Omega$ are connected to a wire $A B$ of uniform resistivity, as shown in the figure. The radius of the wire varies linearly along its axis from $0.2 \mathrm{~mm}$ at $A$ to $1 \mathrm{~mm}$ at $B$. A galvanometer $(\mathrm{G})$ connected to the center of the wire, $50 \mathrm{~cm}$ from each end along its axis, shows zero deflection when $A$ and $B$ are connected to a battery. The value of $X$ is ____________.
Answer
5
Explanation
According to the given condition wire is having different cross-section at two junction. (Frustum shaped conducter)
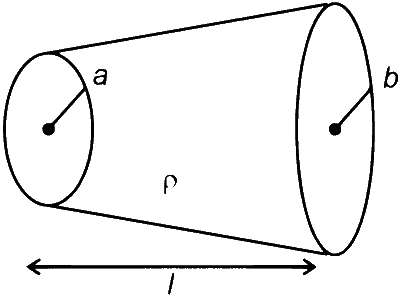
$$ R=\rho \frac{I}{\pi a b} $$
For the shown conductor in the diagram.
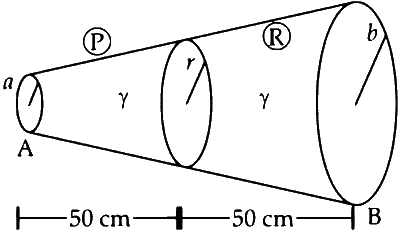
$$ r=\frac{a+b}{2}=\frac{0.2+1}{2}=0.6 $$ .........(i)
As $$ \mathrm{R}=\frac{\rho l}{\mathrm{~A}} $$ ...........(ii)
Hence, Resistence of left $50 \mathrm{~cm}$ wire
$$ =\frac{\rho \times 0.5 \times 10^6}{\pi \times 0.2 \times 0.6} $$
Resistence of Right $50 \mathrm{~cm}$ wire
$$ =\frac{\rho \times 0.5 \times 10^6}{\pi \times 0.6 \times 1} $$
For wheatstone balanced condition
$ \frac{R_1}{P} =\frac{R_2}{Q} \quad\left(R_1=X\right) $
$$ \Rightarrow $$ $ \frac{(X) \times \pi \times 0.2 \times 0.6}{\rho \times 0.5 \times 10^6} =\frac{(1 \pi) \times 0.6 \times 1}{\rho \times 0.5 \times 10^6} $
$$ \Rightarrow $$ $ \frac{(X) \times \pi \times 0.12}{\rho \times 0.5 \times 10^6} =\frac{\pi \times 0.6 \times 1}{\rho \times 0.5 \times 10^6}$
$$ \Rightarrow $$ $X =5$

$$ R=\rho \frac{I}{\pi a b} $$
For the shown conductor in the diagram.

$$ r=\frac{a+b}{2}=\frac{0.2+1}{2}=0.6 $$ .........(i)
As $$ \mathrm{R}=\frac{\rho l}{\mathrm{~A}} $$ ...........(ii)
Hence, Resistence of left $50 \mathrm{~cm}$ wire
$$ =\frac{\rho \times 0.5 \times 10^6}{\pi \times 0.2 \times 0.6} $$
Resistence of Right $50 \mathrm{~cm}$ wire
$$ =\frac{\rho \times 0.5 \times 10^6}{\pi \times 0.6 \times 1} $$
For wheatstone balanced condition
$ \frac{R_1}{P} =\frac{R_2}{Q} \quad\left(R_1=X\right) $
$$ \Rightarrow $$ $ \frac{(X) \times \pi \times 0.2 \times 0.6}{\rho \times 0.5 \times 10^6} =\frac{(1 \pi) \times 0.6 \times 1}{\rho \times 0.5 \times 10^6} $
$$ \Rightarrow $$ $ \frac{(X) \times \pi \times 0.12}{\rho \times 0.5 \times 10^6} =\frac{\pi \times 0.6 \times 1}{\rho \times 0.5 \times 10^6}$
$$ \Rightarrow $$ $X =5$
Comments (0)


