JEE Advance - Physics (2017 - Paper 2 Offline - No. 4)
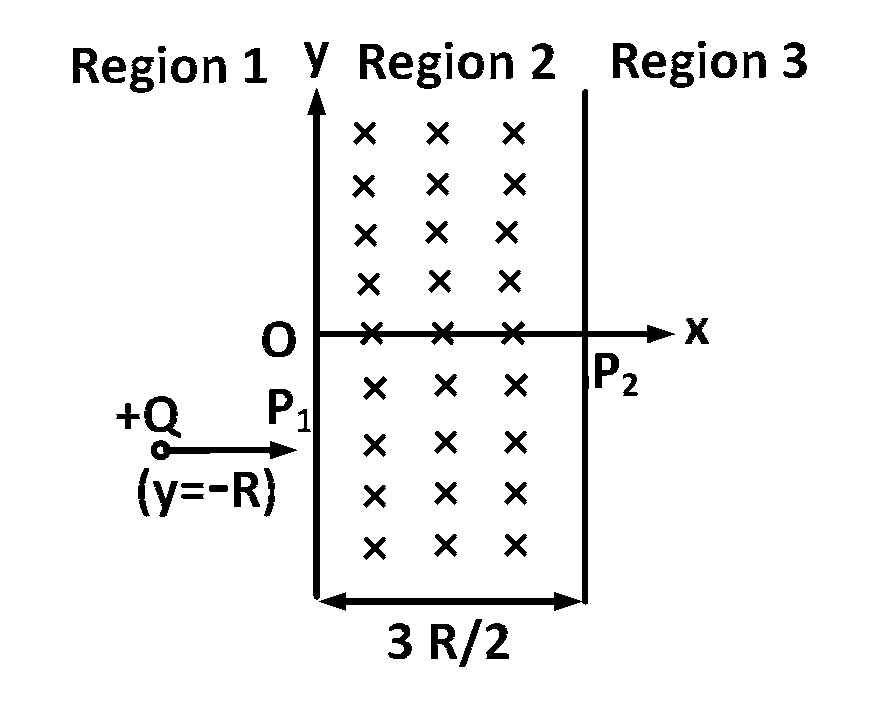
Explanation
As the magnetic field is perpendicular to motion of particle.
$$\therefore$$ Particle will move in curved path of radius,
$$r = {{mv} \over {QB}} = {p \over {QB}}$$ ($$\because$$ p = mv)
Particle will cross the region 2 if
$$r > {{3R} \over 2} \Rightarrow B < {{2p} \over {3QR}}$$
and particle will re-enter region 1 if
$$r < {{3R} \over 2} \Rightarrow B > {{2p} \over {3QR}}$$

Here a = 0, b = (r $$-$$ R)
Equation of trajectory, $${(x - a)^2} + {(y - b)^2} = {r^2}$$
$$\therefore$$ To pass through region 2, at $${P_2}\left( {{{3R} \over 2},0} \right)$$,
$${\left( {{{3R} \over 2}} \right)^2} + {(r - R)^2} = {r^2}$$ or $${9 \over 4}{R^2} + {r^2} + {R^2} - 2rR = {r^2}$$
$${{13} \over 4}{R^2} = 2rR$$ or $$r = {{13} \over 8}R \Rightarrow {p \over {QB}} = {{13} \over 8}R$$ or $$B = {8 \over {13}}{p \over {QR}}$$
Hence, for $$B = {8 \over {13}}{p \over {QR}}$$ particle will enter region 3 through P2
For $$r < {{3R} \over 2}$$, particle will re-enter region 1 through point P3(x, y).
$$y = (2r - R) = \left( {{{2mv} \over {QB}} - R} \right)$$, x = 0
$$\Rightarrow$$ y $$\propto$$ m

At farthest point from y-axis, the momentum is perpendicular to initial momentum.
$$\therefore$$ $$\Delta p = \sqrt 2 mv = \sqrt 2 p$$
Comments (0)


