JEE Advance - Physics (2016 - Paper 1 Offline - No. 8)
A water cooler of storage capacity 120 litres can cool water at a constant rate of P watts. In a closed circulation system (as shown schematically in the figure), the water from the cooler is used to cool an external device that generates constantly 3 kW of heat (thermal load).
The temperature of water fed into the device cannot exceed 30°C and the entire stored 120 litres of water is initially cooled to 10°C. The entire system is thermally insulated. The minimum value of P (in watts) for which the device can be operated for 3 hours is :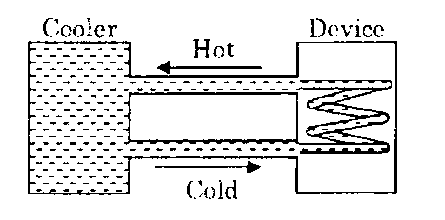
(Specific heat of water is 4.2 kJ kg−1 K−1 and the density of water is 1000 kg m−3)
The temperature of water fed into the device cannot exceed 30°C and the entire stored 120 litres of water is initially cooled to 10°C. The entire system is thermally insulated. The minimum value of P (in watts) for which the device can be operated for 3 hours is :

(Specific heat of water is 4.2 kJ kg−1 K−1 and the density of water is 1000 kg m−3)
1600
2067
2533
3933
Explanation
Heat generated in device in 3 h
= Time $$\times$$ power
= 3 $$\times$$ 3600 $$\times$$ 3 $$\times$$ 103 = 324 $$\times$$ 105 J
Heat used to heat water = ms $$\Delta$$ $$\theta$$
= 120 $$\times$$ 1 $$\times$$ 4.2 $$\times$$ 103 $$\times$$ 20J
Heat absorbed by coolant
Pt = 324 $$\times$$ 105 $$-$$ 120 $$\times$$ 1 $$\times$$ 4.2 $$\times$$ 103 $$\times$$ 20J
Pt = (325 $$-$$ 100.8) $$\times$$ 105 J = 223.2 $$\times$$ 105 J
P = $${{223.2 \times {{10}^5}} \over {3600}}$$ = 2067 W
= Time $$\times$$ power
= 3 $$\times$$ 3600 $$\times$$ 3 $$\times$$ 103 = 324 $$\times$$ 105 J
Heat used to heat water = ms $$\Delta$$ $$\theta$$
= 120 $$\times$$ 1 $$\times$$ 4.2 $$\times$$ 103 $$\times$$ 20J
Heat absorbed by coolant
Pt = 324 $$\times$$ 105 $$-$$ 120 $$\times$$ 1 $$\times$$ 4.2 $$\times$$ 103 $$\times$$ 20J
Pt = (325 $$-$$ 100.8) $$\times$$ 105 J = 223.2 $$\times$$ 105 J
P = $${{223.2 \times {{10}^5}} \over {3600}}$$ = 2067 W
Comments (0)


