JEE Advance - Physics (2015 - Paper 2 Offline - No. 8)
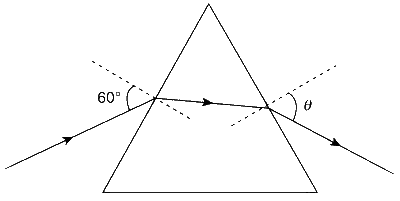
Explanation
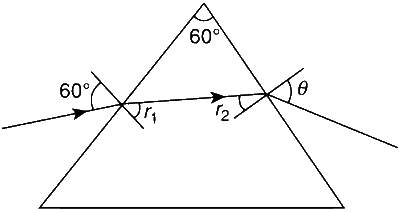
Using Snell's law:
$$\sin 60^\circ = n\sin {r_1}$$ ..... (1)
$$\sin {r_1} = {{\sqrt 3 } \over {2 \times \sqrt 3 }} = {1 \over 2}$$
$${r_1} = 30^\circ $$
Also,
$$n\sin {r_2} = 1\sin \theta $$
Also
$${r_1} + {r_2} = A = 60^\circ $$
Therefore,
$$n\sin (60^\circ - {r_1}) = 1\sin \theta $$ ....... (2)
Differentiating on both sides, we get
$$\sin (60^\circ - {r_1}) - n\cos (60^\circ - {r_1}){{d{r_1}} \over {dn}} = \cos \theta {{d\theta } \over {dn}}$$
Differentiating Eq. (1) on both sides, we get
$$0 = \sin {r_1} + n\cos {r_1}{{d{r_1}} \over {dn}}$$
$$0 = {1 \over 2} + \sqrt 3 .{{\sqrt 3 } \over 2}{{d{r_1}} \over {dn}}$$
Therefore,
$${{d{r_1}} \over {dn}} = {{ - 1} \over 3}$$
Hence, substituting $${r_1} = 30^\circ $$, we get
$${{d{r_1}} \over {dn}} = {{ - 1} \over 3}$$
Now, $$\sin 30^\circ - \sqrt 3 \cos 30^\circ \left( { - {1 \over 3}} \right) = \cos 60^\circ {{d\theta } \over {dn}}$$
$${1 \over 2} + {3 \over {2 \times 3}} = {1 \over 2}{{d\theta } \over {dn}}$$
$${{d\theta } \over {dn}} = 2$$
Comments (0)


