JEE Advance - Physics (2012 - Paper 1 Offline - No. 1)
Explanation
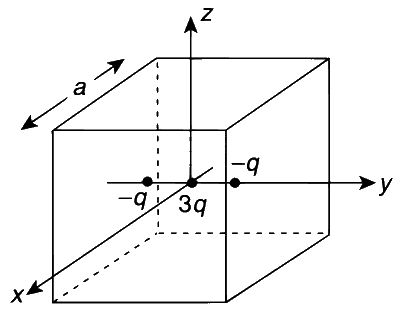
The positions of all charges are symmetric about the planes $$x = +\frac{a}{2}$$ and $$x = -\frac{a}{2}$$. Therefore, the net electric flux crossing the plane $$x = +\frac{a}{2}$$ is equal to the net electric flux crossing the plane $$x = -\frac{a}{2}$$.
Similarly, the net electric flux crossing the plane $$y = +\frac{a}{2}$$ is equal to the net electric flux crossing the plane $$y = -\frac{a}{2}$$.
According to Gauss's law, the net electric flux crossing the entire region is given by:
$$ \phi = \frac{q_{\text{inside}}}{\varepsilon_0} = \frac{3q - q - q}{\varepsilon_0} = \frac{q}{\varepsilon_0} $$
The charges are symmetrically placed about the planes $$z = +\frac{a}{2}$$ and $$x = +\frac{a}{2}$$. Thus, the net electric flux crossing the plane $$z = +\frac{a}{2}$$ is equal to the net electric flux crossing the plane $$x = +\frac{a}{2}$$.
Comments (0)


