JEE Advance - Physics (2010 - Paper 1 Offline - No. 20)
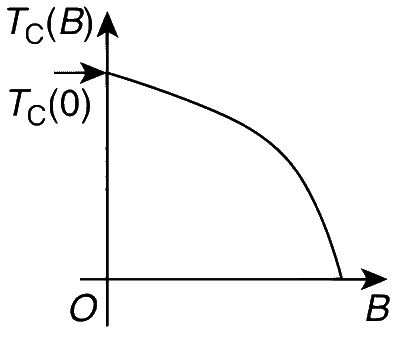
A superconductor has Tc(0) = 100 K. When a magnetic field of 7.5 T is applied, its Tc decreases to 75 K. For this material, one can definitely say that when
B = 5 T, Tc(B) = 80 K
B = 5 T, 75 K < Tc (B) < 100 K
B = 10 T, 75 K < Tc < 100 K
B = 10, Tc = 70 K
Explanation
It is given that Tc(0) = 100 K and Tc(7.5) = 75 K. Since Tc(B) is a monotonically decreasing function of B, Tc(5) < Tc(0) and Tc(5) > Tc(7.5). Thus, 75 K < Tc(5) < 100 K.
Comments (0)