JEE Advance - Physics (2009 - Paper 1 Offline - No. 19)
Column II shows five systems in which two objects are labelled as X and Y. Also in each case a point P is shown. Column I gives some statements about X and/or Y. Match these statements to the appropriate system(s) from Column II:
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
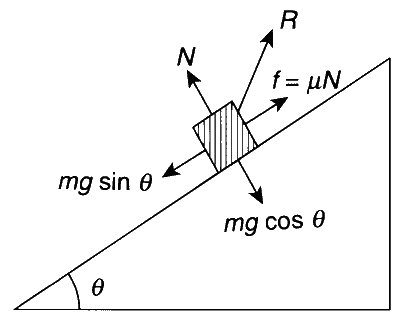
| (A) | The force exerted by X on Y has a magnitude $$Mg$$. | (P) | 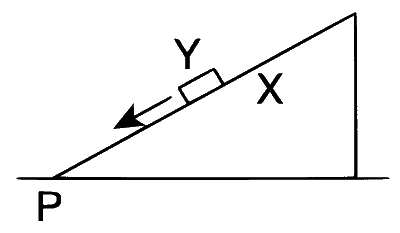 Block Y of mass M left on a fixed inclined plane X, slides on it with a constant velocity. |
| (B) | The gravitational potential energy of X is continuously increasing. | (Q) | 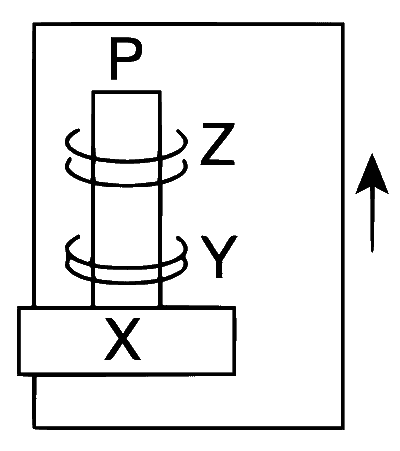 Two rings magnets Y and Z, each of mass M, are kept in frictionless vertical plastic stand so that they repel each other. Y rests on the base X and Z hangs in air in equilibrium. P is the topmost point of the stand on the common axis of the two rings. The whole system is in a lift that is going up with a constant velocity. |
| (C) | Mechanical energy of the system X + Y is continuously decreasing. | (R) | 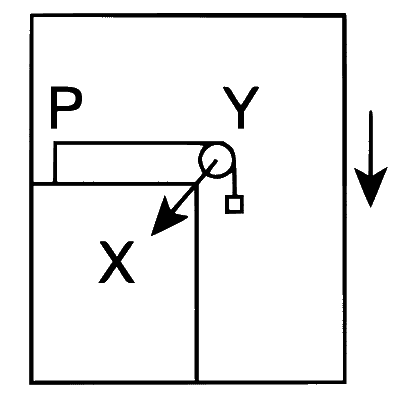 A pulley Y of mass $$m_0$$ is fixed to a table through a clamp X. A block of mass M hangs from a string that goes over the pulley and is fixed at point P of the table. The whole system is kept in a lift that is going down with a constant velocity. |
| (D) | The torque of the weight of Y about point is zero. | (S) | 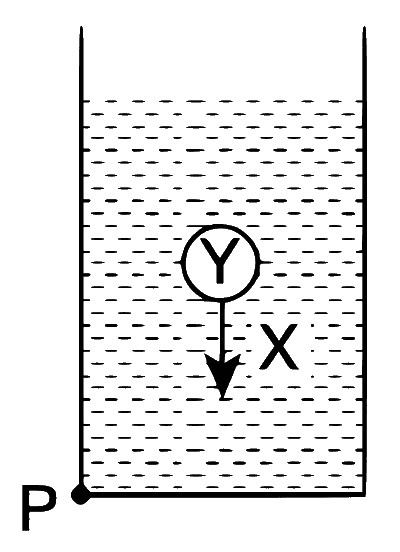 A sphere Y of mass M is put in a non-viscous liquid X kept in a container at rest. The sphere is released and it moves down in the liquid. |
| (T) | 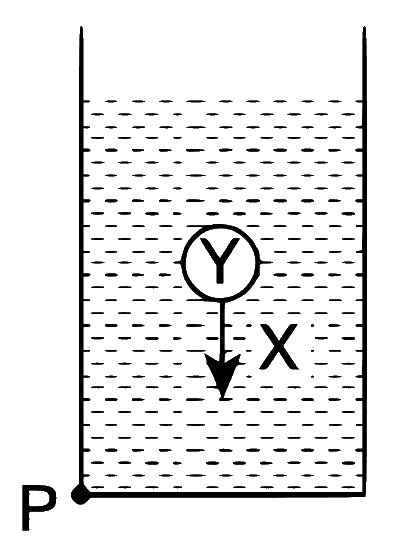 A sphere Y of mass M is falling with its terminal velocity in a viscous liquid X kept in a container. |
Explanation
Case (P) : Since $$v$$ = Constant, we have
$$Mg\sin \theta = \mu Mg\cos \theta = f \Rightarrow \mu = \tan \theta $$
Now, $$N = Mg\cos \theta $$. Therefore,
$$R = \sqrt {{N^2} + {f^2}} = Mg\sqrt {{{\cos }^2}\theta + {{\sin }^2}\theta } $$
Case (T) : We have $$Mg = {F_v} + {F_b}$$, where $${F_v}$$ is the viscous force and $${F_b}$$ is the buoyant force.
Case (S) : We have $$Mg - {F_b} = Ma$$.
Case (R) : We have $$Mg = T$$. Therefore,
$$T + {M_0}g = {F_y}$$ (by the clamp)
$$T = {F_X}$$ (by the clamp)
Therefore, the force exerted by the clamp X on pulley Y is
$$F = \sqrt {F_X^2 + F_Y^2} = g\sqrt {{M^2} + {{(M + {m_0})}^2}} $$
Case (Q) : We have
$$Mg = {F_m}$$ (for Z)
where $${F_m}$$ is the magnetic repulsion. Also,
$$Mg + {F_m} = N$$ (for Y)
Therefore, $$N = 2Mg$$.
Note :
Option (A) : For option (T), if $${F_b}$$ is ignored, then $$Mg = {F_v}$$; otherwise, no case matches for option (A).
Hence, (A) $$\to$$ (T), (P).
Option (B) : In option (Q), it is mentioned that the lift is moving up continuously; therefore, the gravitational potential energy of X goes on increasing. In option (B), as Y comes down, X goes up (displaced). The same is applicable for option (T).
Hence, (B) $$\to$$ (Q), (S), (T).
Option (C) : For option (P), since Y moves down with a constant $$v$$, the gravitational potential energy of the system X + Y goes on decreasing, similar is the case in Options (R) and (T).
Hence, (C) $$\to$$ (P), (R), (T).
Option (D) : For option (S), the mass moves down with acceleration. Therefore, the kinetic energy goes on increasing. Since the line of action of Mg of Y phases through point P, as mentioned in option (Q), its torque about P is zero.
Hence, (D) $$\to$$ (Q).
Comments (0)


