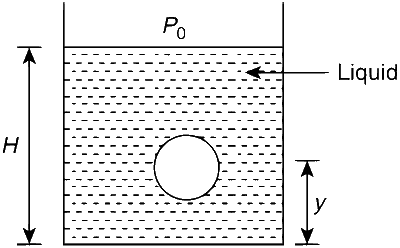
JEE Advance - Physics (2008 - Paper 1 Offline - No. 15)
As the bubble moves upwards, besides the buoyancy force the following forces are acting on it
Only the force of gravity
The force due to gravity and the force due to the pressure of the liquid
The force due to gravity, the force due to the pressure of the liquid and the force due to viscosity of the liquid
The force due to gravity and the force due to viscosity of the liquid
Explanation
As the bubble moves upwards, besides the buoyancy force (the cause of which is pressure difference), only the force of gravity and the force of viscosity will act.
Comments (0)