JEE Advance - Mathematics (2025 - Paper 2 Online - No. 7)
Let $P\left(x_1, y_1\right)$ and $Q\left(x_2, y_2\right)$ be two distinct points on the ellipse
$$ \frac{x^2}{9}+\frac{y^2}{4}=1 $$
such that $y_1>0$, and $y_2>0$. Let $C$ denote the circle $x^2+y^2=9$, and $M$ be the point $(3,0)$.
Suppose the line $x=x_1$ intersects $C$ at $R$, and the line $x=x_2$ intersects C at $S$, such that the $y$-coordinates of $R$ and $S$ are positive. Let $\angle R O M=\frac{\pi}{6}$ and $\angle S O M=\frac{\pi}{3}$, where $O$ denotes the origin $(0,0)$. Let $|X Y|$ denote the length of the line segment $X Y$.
Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
Explanation
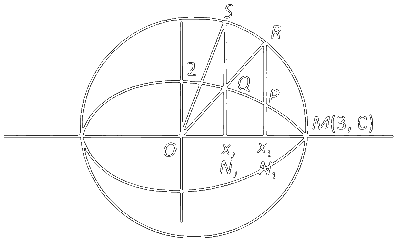
$\begin{aligned} & \mathrm{P} \equiv\left(3 \cos 30^{\circ}, 2 \sin 30^{\circ}\right) \equiv\left(\frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{2}, 1\right) \\ & \mathrm{Q} \equiv\left(3 \cos 60^{\circ}, 2 \sin 60^{\circ}\right) \equiv\left(\frac{3}{2}, \sqrt{3}\right) \\ & \mathrm{R}\left(\frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{2}, \frac{3}{2}\right), \mathrm{S}\left(\frac{3}{2}, \frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{2}\right)\end{aligned}$
Slope of $\mathrm{PQ}=\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{PQ}}=\frac{\sqrt{3}-1}{\frac{3}{2}-\frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{2}}=-\frac{2}{3}$
Equation of line PQ
$$ y-\sqrt{3}=-\frac{2}{3}\left(x-\frac{3}{2}\right) $$
$\Rightarrow 2 x+3 y=3(\sqrt{3}+1) \quad$ option (A) is correct
Now
if $\mathrm{N}_2=\left(\mathrm{x}_2, 0\right)=\left(\frac{3}{2}, 0\right)$
$\left|\mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{Q}\right|=\sqrt{3}$ and $\left|\mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{~S}\right|=\frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow 3\left|\mathrm{~N}_2 \mathrm{Q}\right|=2\left|\mathrm{~N}_2 \mathrm{~S}\right| \quad$ option (C) is correct
Now, if $\mathrm{N}_1=\left(\mathrm{x}_1, 0\right) \Rightarrow \mathrm{N}_1=\left(\frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{2}, 0\right)$
$\Rightarrow\left|\mathrm{N}_1 \mathrm{P}\right|=1,\left|\mathrm{~N}_1 \mathrm{R}\right|=\frac{3}{2} \quad$ option (D) is incorrect
Comments (0)


