JEE Advance - Mathematics (2024 - Paper 2 Online - No. 13)
Let the function $f:[1, \infty) \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ be defined by
$$ f(t)=\left\{\begin{array}{cc} (-1)^{n+1} 2, & \text { if } t=2 n-1, n \in \mathbb{N}, \\ \frac{(2 n+1-t)}{2} f(2 n-1)+\frac{(t-(2 n-1))}{2} f(2 n+1), & \text { if } 2 n-1 < t < 2 n+1, n \in \mathbb{N} . \end{array}\right. $$
Define $g(x)=\int_1^x f(t) d t, x \in(1, \infty)$. Let $\alpha$ denote the number of solutions of the equation $g(x)=0$ in the interval $(1,8]$ and $\beta=\lim \limits_{x \rightarrow l+} \frac{g(x)}{x-1}$.
Then the value of $\alpha+\beta$ is equal to _______.
Explanation
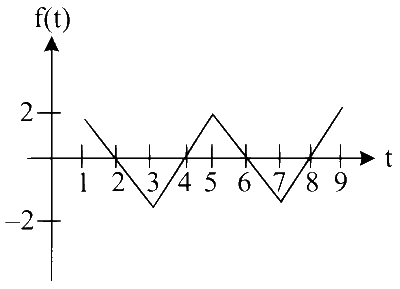
$$\mathrm{f}(\mathrm{t})=\left\{\begin{array}{ccc} 2 & ; & \mathrm{t}=1 \\ 4-2 \mathrm{t} & ; & 1<\mathrm{t}<3 \\ -2 & ; & \mathrm{t}=3 \\ -8-2 \mathrm{t} & ; & 3<\mathrm{t}<5 \\ 2 & ; & \mathrm{t}=5 \\ 12-2 \mathrm{t} & ; & 5<\mathrm{t}<7 \\ -2 & ; & \mathrm{t}=7 \\ -16+2 \mathrm{t} & ; & 7<\mathrm{t}<9 \end{array}\right.$$
$$\begin{aligned} & g(x)=\int_\limits1^x f(t) d t ; g^{\prime}(x)=f(x) \\ & \text { for } x \in(1,8] \\ & g(x)=0 \Rightarrow x=3,5,7 \therefore \alpha=3 \\ & \beta=\lim _{x \rightarrow 1^{+}} \frac{g(x)}{x-1} \end{aligned}$$
Apply L'pital
$$\begin{aligned} & =\frac{g^{\prime}\left(1^{+}\right)}{1}=f\left(1^{+}\right) \\ & \beta=2 \\ & \therefore \alpha+\beta=5 \end{aligned}$$
Comments (0)


