JEE Advance - Mathematics (2024 - Paper 1 Online - No. 17)
Let $f: \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ and $g: \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ be functions defined by
$$ f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} x|x| \sin \left(\frac{1}{x}\right), & x \neq 0, \\ 0, & x=0, \end{array} \quad \text { and } g(x)= \begin{cases}1-2 x, & 0 \leq x \leq \frac{1}{2}, \\ 0, & \text { otherwise } .\end{cases}\right. $$
Let $a, b, c, d \in \mathbb{R}$. Define the function $h: \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ by
$$ h(x)=a f(x)+b\left(g(x)+g\left(\frac{1}{2}-x\right)\right)+c(x-g(x))+d g(x), x \in \mathbb{R} . $$
Match each entry in List-I to the correct entry in List-II.
| List-I | List-II |
|---|---|
| (P) If $a = 0$, $b = 1$, $c = 0$, and $d = 0$, then | (1) $h$ is one-one. |
| (Q) If $a = 1$, $b = 0$, $c = 0$, and $d = 0$, then | (2) $h$ is onto. |
| (R) If $a = 0$, $b = 0$, $c = 1$, and $d = 0$, then | (3) $h$ is differentiable on $\mathbb{R}$. |
| (S) If $a = 0$, $b = 0$, $c = 0$, and $d = 1$, then | (4) the range of $h$ is $[0, 1]$. |
| (5) the range of $h$ is $\{0, 1\}$. |
The correct option is
Explanation
$$f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cc} x|x| \sin \frac{1}{x} & ; x \neq 0 \\ 0 & ; \quad x=0 \end{array} \quad g(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cc} 1-2 x & 0 \leq x \leq \frac{1}{2} \\ 0 ; & \text { otherwise } \end{array}\right.\right.$$
$$g\left(\frac{1}{2}-x\right)=\left\{\begin{array}{cc} 2 x & ; \quad 0 \leq \frac{1}{2}-x \leq \frac{1}{2} \\ 0 ; & \text { otherwise } \end{array}=\left\{\begin{array}{cc} 2 x ; & 0 \leq x \leq \frac{1}{2} \\ 0 ; & \text { otherwise } \end{array}\right\}\right.$$
$$g(x)+g\left(\frac{1}{2}-x\right)=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} 1 ; & 0 \leq x \leq \frac{1}{2} \\ 0 & ; \text { otherwise } \end{array}\right\}$$
(P) $$\quad$$ Now $$a=0, b=1, c=0, d=0$$
$$\because h(x)=g(x)+g\left(\frac{1}{2}-x\right)= \begin{cases}1 ; & 0 \leq x \leq \frac{1}{2} \\ 0 ; & \text { otherwise }\end{cases}$$
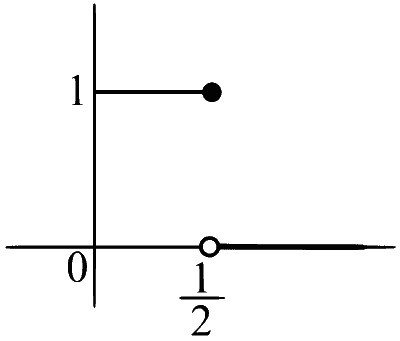
Hence Range of h(x) is {0, 1}
(Q) $$\mathrm{a}=1, \mathrm{~b}=0, \mathrm{c}=0, \mathrm{~d}=0$$
$$h(x)=f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cc} x|x| \sin \frac{1}{x} & ; x \neq 0 \\ 0 & ; x=0 \end{array}\right.$$
$$\begin{aligned} & R H D=\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{x^2 \sin \frac{1}{x}-0}{x}=0 \\ & \text { LHD }=\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{-x^2 \sin \frac{1}{x}-0}{x}=0 \end{aligned}$$
Hence $$h(x)$$ is differentiable on $$R$$
(R) $$\mathrm{a}=0, \mathrm{~b}=0, \mathrm{c}=1, \mathrm{~d}=0$$
$$h(x)=x-g(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cl} 3 x-1 & ; 0 \leq x \leq \frac{1}{2} \\ 0 ; & \text { otherwise } \end{array}\right.$$
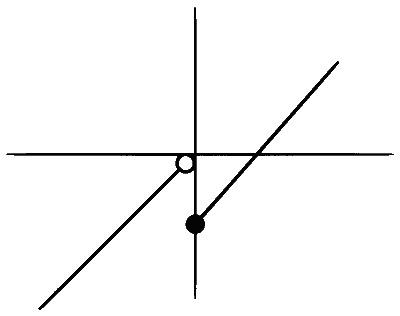
$$\therefore \mathrm{h}(\mathrm{x}) \text { is ONTO }$$
(S) $$a=0, b=0, c=0, d=1$$
$$h(x)=g(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cl} 1-2 x & ; 0 \leq x \leq \frac{1}{2} \\ 0 ; & \text { otherwise } \end{array}\right.$$
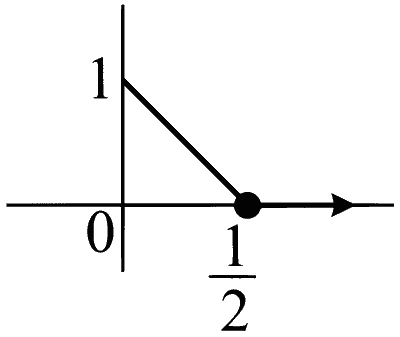
Range of h(x) is [0, 1]
Comments (0)


