JEE Advance - Mathematics (2023 - Paper 2 Online - No. 9)
For $x \in \mathbb{R}$, let $y(x)$ be a solution of the differential equation
$\left(x^2-5\right) \frac{d y}{d x}-2 x y=-2 x\left(x^2-5\right)^2$ such that $y(2)=7$.
Then the maximum value of the function $y(x)$ is :
$\left(x^2-5\right) \frac{d y}{d x}-2 x y=-2 x\left(x^2-5\right)^2$ such that $y(2)=7$.
Then the maximum value of the function $y(x)$ is :
Answer
16
Explanation
$\begin{aligned} &\left(x^2-5\right) \frac{d y}{d x}-2 x y =-2 x\left(x^2-5\right)^2 \\ \\& \Rightarrow \frac{d y}{d x}-\frac{2 x}{\left(x^2-5\right)} y=-2 x\left(x^2-5\right)\end{aligned}$
I.F. $=e^{-\int \frac{2 x}{x^2-5} d x}=\frac{1}{\left(x^2-5\right)}$
Now
$$ \begin{aligned} y \cdot \frac{1}{\left(x^2-5\right)} & =-\int 2 x d x \\\\ & =-x^2+c \end{aligned} $$
$\begin{array}{rlrl} &\Rightarrow y =c\left(x^2-5\right)-x^2\left(x^2-5\right) \\\\ & y(2) =7 \\\\ &\Rightarrow 7 =-c+4 \\\\ &\Rightarrow c=-3\end{array}$
So,
$$ \begin{aligned} y & =\left(x^2-5\right)\left(-x^2-3\right) ............(1) \\\\ \frac{d y}{d x} & =\left(x^2-5\right)(-2 x)+\left(-x^2-3\right)(2 x) \\\\ & =2 x\left(-x+5-x^2-3\right) \\\\ & =2 x\left(-2 x^2+2\right) \end{aligned} $$
For maxima and minima, put $\frac{d y}{d x}=0$
$\Rightarrow x=0, \pm 1$
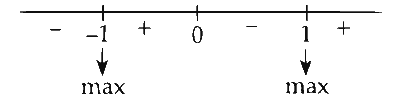
From (1),
$$ y_{\text {max }}=16 $$
I.F. $=e^{-\int \frac{2 x}{x^2-5} d x}=\frac{1}{\left(x^2-5\right)}$
Now
$$ \begin{aligned} y \cdot \frac{1}{\left(x^2-5\right)} & =-\int 2 x d x \\\\ & =-x^2+c \end{aligned} $$
$\begin{array}{rlrl} &\Rightarrow y =c\left(x^2-5\right)-x^2\left(x^2-5\right) \\\\ & y(2) =7 \\\\ &\Rightarrow 7 =-c+4 \\\\ &\Rightarrow c=-3\end{array}$
So,
$$ \begin{aligned} y & =\left(x^2-5\right)\left(-x^2-3\right) ............(1) \\\\ \frac{d y}{d x} & =\left(x^2-5\right)(-2 x)+\left(-x^2-3\right)(2 x) \\\\ & =2 x\left(-x+5-x^2-3\right) \\\\ & =2 x\left(-2 x^2+2\right) \end{aligned} $$
For maxima and minima, put $\frac{d y}{d x}=0$
$\Rightarrow x=0, \pm 1$
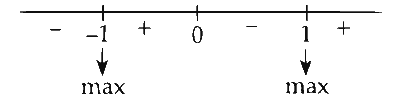
From (1),
$$ y_{\text {max }}=16 $$
Comments (0)


