JEE Advance - Mathematics (2023 - Paper 1 Online - No. 8)
Let $\tan ^{-1}(x) \in\left(-\frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2}\right)$, for $x \in \mathbb{R}$. Then the number of real solutions of the equation $\sqrt{1+\cos (2 x)}=\sqrt{2} \tan ^{-1}(\tan x)$ in the set $\left(-\frac{3 \pi}{2},-\frac{\pi}{2}\right) \cup\left(-\frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2}\right) \cup\left(\frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{3 \pi}{2}\right)$ is equal to :
Answer
3
Explanation
$\sqrt{1+\cos 2 x}=\sqrt{2} \tan ^{-1}(\tan x)$
$\begin{aligned} & \Rightarrow \sqrt{2 \cos ^2 x}=\sqrt{2} \tan ^{-1} \tan x \\\\ & \Rightarrow \sqrt{2}|\cos x|=\sqrt{2} \tan ^{-1} \tan x \\\\ & \Rightarrow |\cos x|=\tan ^{-1} \tan x\end{aligned}$
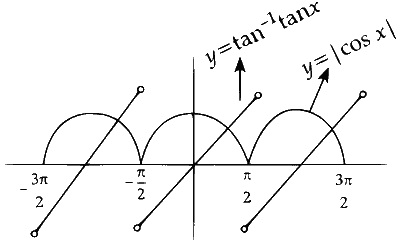
Number of solution $=3$.
$\begin{aligned} & \Rightarrow \sqrt{2 \cos ^2 x}=\sqrt{2} \tan ^{-1} \tan x \\\\ & \Rightarrow \sqrt{2}|\cos x|=\sqrt{2} \tan ^{-1} \tan x \\\\ & \Rightarrow |\cos x|=\tan ^{-1} \tan x\end{aligned}$

Number of solution $=3$.
Comments (0)


