JEE Advance - Mathematics (2022 - Paper 2 Online - No. 8)
$$ f(x)=x^{2}+\frac{5}{12} \quad \text { and } \quad g(x)= \begin{cases}2\left(1-\frac{4|x|}{3}\right), & |x| \leq \frac{3}{4} \\ 0, & |x|>\frac{3}{4}\end{cases} $$
If $\alpha$ is the area of the region
$$ \left\{(x, y) \in \mathbb{R} \times \mathbb{R}:|x| \leq \frac{3}{4}, 0 \leq y \leq \min \{f(x), g(x)\}\right\}, $$
then the value of $9 \alpha$ is
Explanation
$$f(x) = {x^2} + {5 \over {12}}$$
This represent upward parabola.
$$g(x) = 2\left( {1 - {{4|x|} \over 3}} \right)$$
At $$x = 0$$
$$g(0) = 2$$
At $$x = {3 \over 4}$$
$$g\left( {{3 \over 4}} \right) = 0$$
$$\therefore$$ Graph is
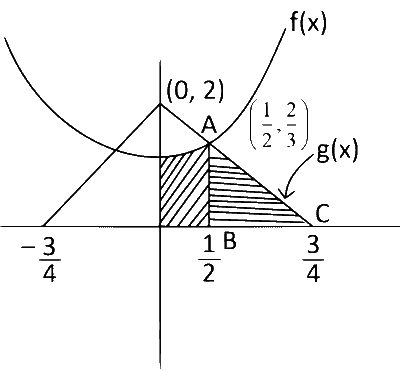
Intersection point of f(x) and g(x) at first quadrant,
$$f(x) = g(x)$$
$$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {5 \over {12}} = 2\left( {1 - {{4x} \over 3}} \right)$$ [ $$|x| = x$$ as in first quadrant $$x > 0$$ ]
$$ \Rightarrow 12{x^2} + 5 = 24 - 32x$$
$$ \Rightarrow 12{x^2} + 32x - 19 = 0$$
$$ \Rightarrow 12{x^2} + 38x - 6x - 19 = 0$$
$$ \Rightarrow 2x(6x + 19) - 1(6x + 19) = 0$$
$$ \Rightarrow (2x - 1)(6x + 19) = 0$$
$$\therefore$$ $$x = {1 \over 2},\, - {{19} \over 6}$$
In first quadrant $$x = {1 \over 2}$$
When $$x = {1 \over 2}$$,
$$y = {\left( {{1 \over 2}} \right)^2} + {5 \over {12}} = {2 \over 3}$$
$$\therefore$$ Area $$A = 2$$ ( $$\int\limits_0^{{1 \over 2}} {\left( {{x^2} + {5 \over {12}}} \right)dx + } $$ Area of $$\Delta ABC$$ )
$$ = 2\left[ {\int\limits_0^{{1 \over 2}} {\left( {{x^2} + {5 \over {12}}} \right)dx + {1 \over 2} \times \left( {{3 \over 4} - {1 \over 2}} \right) \times {2 \over 3}} } \right]$$
$$ = 2\left[ {\left[ {{{{x^3}} \over 3} + {{5x} \over {12}}} \right]_0^{{1 \over 2}} + {1 \over 2} \times {1 \over 4} \times {2 \over 3}} \right]$$
$$ = 2\left[ {\left( {{1 \over {24}} + {5 \over {12}} \times {1 \over 2}} \right) + {1 \over {12}}} \right]$$
$$ = 2\left[ {{1 \over {24}} + {5 \over {24}} + {2 \over {24}}} \right]$$
$$ = 2\left[ {{{1 + 5 + 2} \over {24}}} \right]$$
$$ = 2 \times {8 \over {24}}$$
$$ = {2 \over 3} = \alpha $$
$$\therefore$$ $$ = 9\alpha = {2 \over 3} \times 9 = 6$$
Comments (0)


