JEE Advance - Mathematics (2012 - Paper 1 Offline - No. 6)
Explanation
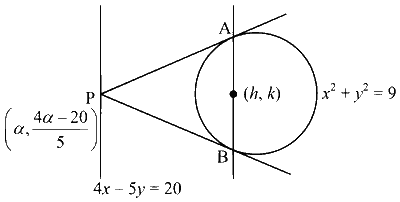
Equation of the chord AB is $$\mathrm{T}=0$$
$$\Rightarrow \alpha x+\left(\frac{4 \alpha-20}{5}\right) y=9\quad \text{... (i)}$$
Also, equation of the chord AB whose mid-point is $$(h, k)$$ is $$\mathrm{T}=\mathrm{S}_1$$
$$\begin{aligned} & \Rightarrow \quad h x+k y-9=h^2+k^2-9 \\ & \Rightarrow \quad h x+k y=h^2+k^2 \quad \text{... (ii)} \end{aligned}$$
$$\because$$ Equations (i) and (ii) both represent the same line
$$\begin{aligned} & \therefore \frac{\alpha}{h}=\frac{\frac{4 \alpha-20}{5}}{k}=\frac{9}{h^2+k^2} \\ & \Rightarrow \alpha=\frac{9 h}{h^2+k^2} \quad \text { and } \quad \frac{4 \alpha-20}{5}=\frac{9 k}{h^2+k^2} \end{aligned}$$
$$\begin{aligned} & \Rightarrow \alpha=\frac{9 h}{h^2+k^2} \quad \text { and } \quad 4 \alpha=\frac{45 k}{h^2+k^2}+20 \\ & \Rightarrow \alpha=\frac{9 h}{h^2+k^2} \quad \text { and } \quad \alpha=\frac{45 k+20\left(h^2+k^2\right)}{4\left(h^2+k^2\right)} \end{aligned}$$
$$\begin{array}{ll} \Rightarrow & \frac{9 h}{h^2+k^2}=\frac{45 k+20\left(h^2+k^2\right)}{4\left(h^2+k^2\right)} \\ \Rightarrow & 36 h=45 k+20\left(h^2+k^2\right) \end{array}$$
$$\Rightarrow 20\left(x^2+y^2\right)-36 x+45 y=0$$, which is the required locus.
Comments (0)


