JEE Advance - Chemistry (2024 - Paper 1 Online - No. 14)
In a conductometric titration, small volume of titrant of higher concentration is added stepwise to a larger volume of titrate of much lower concentration, and the conductance is measured after each addition.
The limiting ionic conductivity $\left(\Lambda_0\right)$ values (in $\mathrm{mS} \mathrm{m}{ }^2 \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$ ) for different ions in aqueous solutions are given below:
$$ \begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline \text { Ions } & \mathrm{Ag}^{+} & \mathrm{K}^{+} & \mathrm{Na}^{+} & \mathrm{H}^{+} & \mathrm{NO}_3^{-} & \mathrm{Cl}^{-} & \mathrm{SO}_4^{2-} & \mathrm{OH}^{-} & \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COO}^{-} \\ \hline \Lambda_0 & 6.2 & 7.4 & 5.0 & 35.0 & 7.2 & 7.6 & 16.0 & 19.9 & 4.1 \\ \hline \end{array} $$
For different combinations of titrates and titrants given in List-I, the graphs of 'conductance' versus 'volume of titrant' are given in List-II.
Match each entry in List-I with the appropriate entry in List-II and choose the correct option.
| LIST-I | LIST-II |
|---|---|
| (P) Titrate: KCl Titrant: AgNO$_3$ |
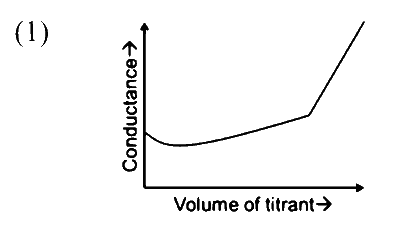
|
| (Q) Titrate: AgNO$_3$ Titrant: KCl |

|
| (R) Titrate: NaOH Titrant: HCl |
|
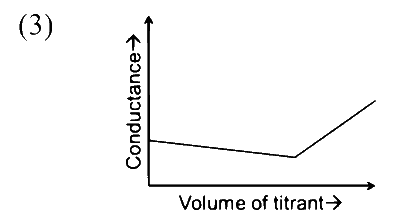
| (S) Titrate: NaOH Titrant: CH$_3$COOH |

|

|
Explanation
Option (P) :
On adding $\mathrm{AgNO}_3$ solution to $\mathrm{KCl}$ solution precipitation of $\mathrm{AgCl}$ will occur due to which $\mathrm{Cl}^{-}$already present will be replaced by $\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}$ions. So conductance of solution will decrease till equivalence point. After complete precipitation of $\mathrm{AgCl}$, further added $\mathrm{AgNO}_3$ will increase the number of ions in resulting solution so conductance will increase.
Option (Q) :
On adding $\mathrm{KCl}$ solution to $\mathrm{AgNO}_3$ solution precipitation of $\mathrm{AgCl}$ will occur due to which already present $\mathrm{Ag}^{+}$ions will be replaced by $\mathrm{K}^{+}$ions in solution. So conductance of solution will increase. After complete precipitation of $\mathrm{AgCl}$ further added $\mathrm{KCl}$ will increase the number of ions in resulting solution so conductance will increase further.
Option (R) :
On adding $\mathrm{HCl}$ solution to $\mathrm{NaOH}$ solution, $\mathrm{OH}^{-}$will be replaced by $\mathrm{Cl}^{-}$ions so conductance of solution decreases. After complete neutralisation further added $\mathrm{HCl}$ will increase number of ions in the solution. So conductance will increase futher.
Option (S) :
On adding $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}$ solution to $\mathrm{NaOH}$ solution $\mathrm{OH}^{-}$will be replaced by $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COO}^{-}$ions, so conductance of solution decreases. After complete neutralisation further added $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}$ will remain undissociated because it is a weak acid and there is also common ion effect on acetate ions. So number of ions in solution will remain almost constant therefore conductance of solution will remain constant.
Comments (0)


