JEE Advance - Chemistry (2020 - Paper 2 Offline - No. 13)
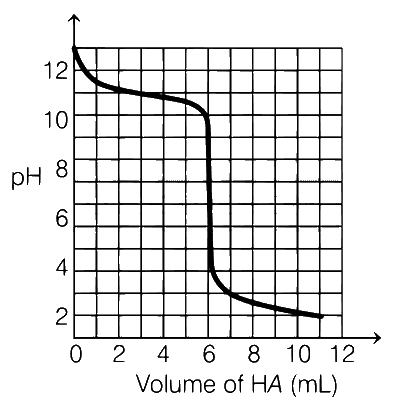
A solution of 0.1 M weak base (B) is titrated with 0.1 M of a strong acid (HA). The variation of pH of the solution with the volume of HA added is shown in the figure below. What is the pKb of the base? The neutralisation reaction is given by
$$B + HA\buildrel {} \over \longrightarrow B{H^ + } + {A^ - }$$
$$B + HA\buildrel {} \over \longrightarrow B{H^ + } + {A^ - }$$

Answer
3
Explanation
From the given diagram, 63 mL volume of HA used till equivalence point. At half of equivalence point, solution will be basic buffer with B and BH+.
$$pOH = p{K_b} + \log {{[B{H^ + }]} \over {[B]}}$$
At half equivalence point :
[BH+] = [B] ($$ \because $$ pH = 11)
Therefore, pOH = pKb = 14 $$-$$ 11 = 3
$$ \because $$ pKb = 3.00
$$pOH = p{K_b} + \log {{[B{H^ + }]} \over {[B]}}$$
At half equivalence point :
[BH+] = [B] ($$ \because $$ pH = 11)
Therefore, pOH = pKb = 14 $$-$$ 11 = 3
$$ \because $$ pKb = 3.00
Comments (0)


