JEE Advance - Chemistry (2018 - Paper 2 Offline - No. 15)
Dilution processes of different aqueous solutions, with water, are given in LIST - I. The effects of dilution of the solutions on $$\left[ {{H^ + }} \right]$$ are given in LIST - II
(Note: Degree of dissociation (a) of weak acid and weak base is $$<<1;$$ degree of hydrolysis of salt $$<<1;$$ $$\left[ {{H^ + }} \right]$$ represents the concentration of $${H^ + }$$ ions)
Match each process given in LIST-I with one or more effect(s) in LIST-II. The correct option is :
(Note: Degree of dissociation (a) of weak acid and weak base is $$<<1;$$ degree of hydrolysis of salt $$<<1;$$ $$\left[ {{H^ + }} \right]$$ represents the concentration of $${H^ + }$$ ions)
| LIST-I | LIST-II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| P. | (10 mL of 0.1 M NaOH + 20 mL of 0.1 M acetic acid) diluted to 60 mL |
1. | the value of [H+] does not change on dilution |
| Q. | (20 mL of 0.1 M NaOH + 20 mL of 0.1 M acetic acid) diluted to 80 mL |
2. | the value of [H+] changes to half of its initial value on dilution |
| R. | (20 mL of 0.1 M HCL + 20 mL of 0.1 M ammonia solution) diluted to 80 mL |
3. | the value of [H+] changes to two times of its initial value on dilution |
| S. | 10 mL saturated solution of Ni(OH)2 in equilibrium with excess solid Ni(OH)2 is diluted to 20 mL (solid Ni(OH)2 is still present after dilution). |
4. | the value of [H+] changes to $${1 \over {\sqrt 2 }}$$ times of its initial value on dilution |
| 5. | the value of [H+] changes to $$\sqrt 2 $$ times of its initial value on dilution |
Match each process given in LIST-I with one or more effect(s) in LIST-II. The correct option is :
$$P - 4;Q - 2;R - 3;S - 1$$
$$P - 4;Q - 3;R - 2;S - 3$$
$$P - 1;Q - 4;R - 5;S - 3$$
$$P - 1;Q - 5;R - 4;S - 1$$
Explanation
P. Sodium hydroxide reacts with acetic acid to form sodium acetate.
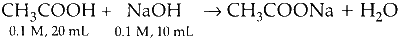
The final solution will be a buffer of $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}$ and $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COONa}$ as $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}$ is not completely neutralised by $\mathrm{NaOH}$.
The final moles of $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}=$ moles of $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COONa}$ = 0.001 mol
$$ \mathrm{Ph}=p \mathrm{~K}_a+\log \frac{\left[\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COO}^{-}\right]}{\left[\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}\right]} $$
$\Rightarrow\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]$will not change on dilution as concentration of salt and acid does not change on dilution.
$\therefore$ Correct match $\mathrm{P}-1$
Q.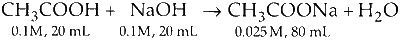
$$ \begin{aligned} & \left[\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COO}^{-}\right]_{\mathrm{old}}=\frac{20 \times 0.1}{40}=\frac{2}{40} \\\\ & {\left[\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COO}^{-}\right]_{\text {new }}=\frac{2}{80}} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} {\left[\mathrm{OH}^{-}\right] } & =\sqrt{\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{H}} \mathrm{C}} \\\\ & =\sqrt{\left(\frac{\mathrm{K}_w}{\mathrm{~K}_a} \mathrm{C}\right)} \\\\ {\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]_1 } & =\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{K}_w \mathrm{~K}_a}{\mathrm{C}}} \\\\ \frac{\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]_2}{\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]_1}=\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{C}_1}{\mathrm{C}_2}} & =\sqrt{\frac{0.05}{0.025}}=\sqrt{2} \end{aligned} $$
Correct match Q-5
R.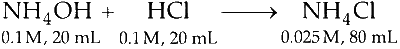
As per the condition given in $R$ the resultant solution before dilution contains 2 millimoles of $\mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{Cl}$ in $40 \mathrm{~mL}$ of solution. Hence, a salt of strong acid and weak base is formed. For this,
$$ \left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]_{\text {initial }}=\sqrt{\frac{K_w \times C}{K_b}} $$
Now on dilution upto $80 \mathrm{~mL}$ new conc. becomes $C / 2$.
So $$ \left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]_{\text {new }}=\sqrt{\frac{K_w \times \frac{C}{2}}{K_b}} $$
or $$ \left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]_{\text {new }}=\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]_{\text {initial }} \times \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} $$
(S) For a saturated solution,
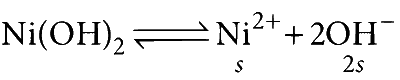
$$ \begin{aligned} K_{s p}=s \times(2 s)^2=4 s^3 \\\\ \Rightarrow s=\left[\mathrm{OH}^{-}\right]=\sqrt[3]{\frac{K_{s p}}{4}} \end{aligned} $$
Irrespective of volume of solution, $\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]$remains constant.
(S) $\rightarrow$ (1)
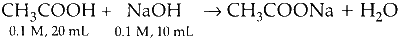
The final solution will be a buffer of $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}$ and $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COONa}$ as $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}$ is not completely neutralised by $\mathrm{NaOH}$.
The final moles of $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}=$ moles of $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COONa}$ = 0.001 mol
$$ \mathrm{Ph}=p \mathrm{~K}_a+\log \frac{\left[\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COO}^{-}\right]}{\left[\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}\right]} $$
$\Rightarrow\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]$will not change on dilution as concentration of salt and acid does not change on dilution.
$\therefore$ Correct match $\mathrm{P}-1$
Q.
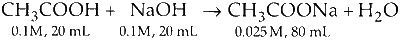
$$ \begin{aligned} & \left[\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COO}^{-}\right]_{\mathrm{old}}=\frac{20 \times 0.1}{40}=\frac{2}{40} \\\\ & {\left[\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COO}^{-}\right]_{\text {new }}=\frac{2}{80}} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} {\left[\mathrm{OH}^{-}\right] } & =\sqrt{\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{H}} \mathrm{C}} \\\\ & =\sqrt{\left(\frac{\mathrm{K}_w}{\mathrm{~K}_a} \mathrm{C}\right)} \\\\ {\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]_1 } & =\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{K}_w \mathrm{~K}_a}{\mathrm{C}}} \\\\ \frac{\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]_2}{\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]_1}=\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{C}_1}{\mathrm{C}_2}} & =\sqrt{\frac{0.05}{0.025}}=\sqrt{2} \end{aligned} $$
Correct match Q-5
R.
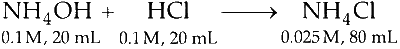
As per the condition given in $R$ the resultant solution before dilution contains 2 millimoles of $\mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{Cl}$ in $40 \mathrm{~mL}$ of solution. Hence, a salt of strong acid and weak base is formed. For this,
$$ \left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]_{\text {initial }}=\sqrt{\frac{K_w \times C}{K_b}} $$
Now on dilution upto $80 \mathrm{~mL}$ new conc. becomes $C / 2$.
So $$ \left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]_{\text {new }}=\sqrt{\frac{K_w \times \frac{C}{2}}{K_b}} $$
or $$ \left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]_{\text {new }}=\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]_{\text {initial }} \times \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} $$
(S) For a saturated solution,
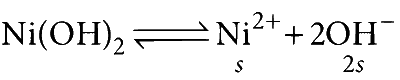
$$ \begin{aligned} K_{s p}=s \times(2 s)^2=4 s^3 \\\\ \Rightarrow s=\left[\mathrm{OH}^{-}\right]=\sqrt[3]{\frac{K_{s p}}{4}} \end{aligned} $$
Irrespective of volume of solution, $\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]$remains constant.
(S) $\rightarrow$ (1)
Comments (0)


