JEE Advance - Chemistry (2017 - Paper 1 Offline - No. 15)
The only CORRECT combination that gives two different carboxylic acids is :
(II) (iv) (R)
(IV) (iii) (Q)
(III) (iii) (P)
(I) (i) (S)
Explanation

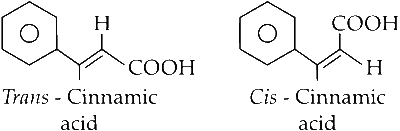
Reaction of benzaldehyde with acetic anhydride in presence of potassium acetate results in formation of cinnamic acid. Cinnamic acid contains cis and trans forms; hence, two types of acids are generated. This is called Perkin reaction.
Mechanism of Perkin reaction is as follows :
(i) The potassium acetate is a strong base and abstracts acidic $\alpha$-proton from acetic anhydride.

(ii) The negatively charged carbanion attacks the carbon of carbonyl group of benzaldehyde.


(iii) The intermediate formed undergoes rearrangement

(iv) Loss of proton from $\alpha$-carbon gives cinnamic acid
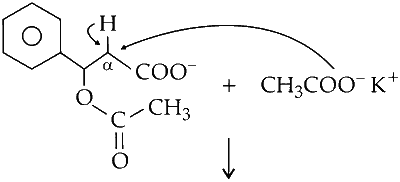
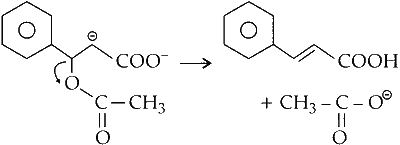
(v) Depending upon the orientation of carboxylic functional group cis and trans cinnamic acid are formed.
Comments (0)


