JEE Advance - Chemistry (2013 - Paper 2 Offline - No. 14)
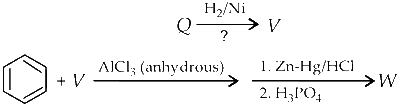
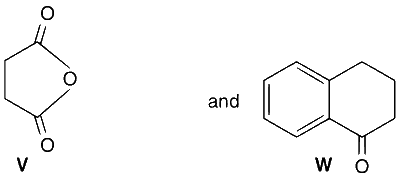
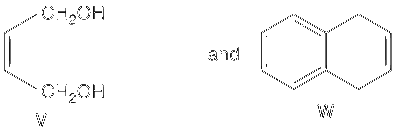
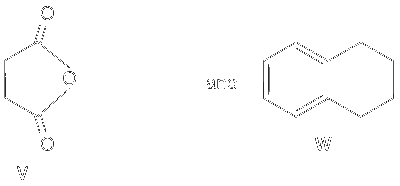
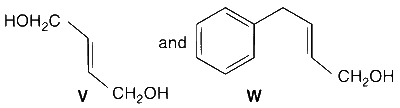
In the following reaction sequences V and W are, respectively,
Explanation
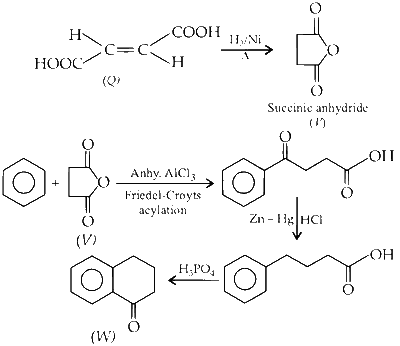
The reactions involved are
Comments (0)

In the following reaction sequences V and W are, respectively,





The reactions involved are

