JEE Advance - Chemistry (2012 - Paper 1 Offline - No. 5)
Explanation
The stability of lyophobic colloidal particles is generally due to two main factors:
Preferential Adsorption: The same charge (either positive or negative) is preferentially adsorbed onto the surface of lyophobic particles, preventing them from coming close to each other and precipitating. For instance, when a dilute solution of silver nitrate is mixed with potassium iodide, it forms a white precipitate of silver iodide. The iodide ions are preferentially adsorbed onto the silver iodide particles, making the sol negatively charged. These negatively charged particles repel each other, thus preventing precipitation.
Electrostatic Layers: Negatively charged sol particles attract positive charges from the surrounding medium, forming a second layer of positive charges around them. This results in two layers of opposite charges, known as the fixed layer and the diffused layer. The potential difference between these oppositely charged layers is referred to as electrokinetic potential or zeta potential.
Here is a visual illustration of the concept (known as Helmholtz double layer):
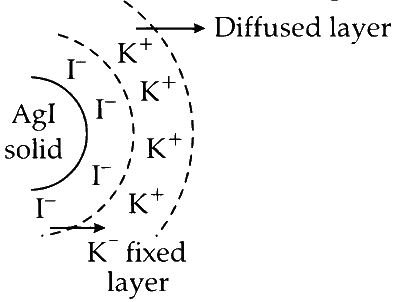
This double layer of opposite charges around the colloidal particles is crucial in maintaining their stability.
Comments (0)


