JEE Advance - Chemistry (2011 - Paper 2 Offline - No. 20)
Match the reactions in Column I with appropriate types of steps/reactive intermediate involved in these reactions as given in Column II :
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | 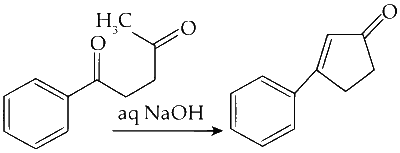 |
(P) | Nucleophilic substitution |
| (B) | 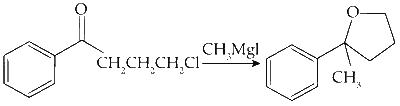 |
(Q) | Electrophilic substitution |
| (C) | 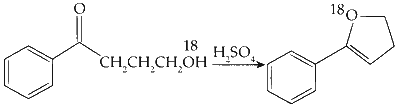 |
(R) | Dehydration |
| (D) | 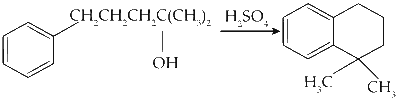 |
(S) | Nucleophilic |
| (T) | Carbanion |
Explanation
(A)
The compound undergoes an intramolecular aldol condensation reaction in the presence of aqueous NaOH.
Steps Involved :
Abstraction of Proton :
The proton attached to the alpha carbon is abstracted, generating a carbanion.
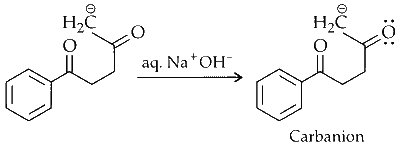
Nucleophilic Addition :
The carbanion attacks the electropositive carbonyl carbon, forming a cyclic intermediate.
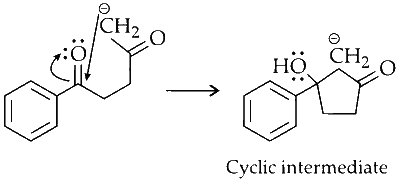
Dehydration :
The cyclic intermediate undergoes dehydration to yield the final product.
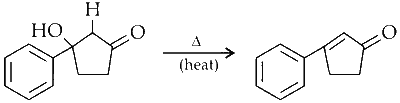
Option (A) in Column I matches with (R), (S), and (T) in Column II.
(B)
Nucleophilic Addition :
The ketone reacts with methyl magnesium bromide, forming a secondary alcohol. This is a nucleophilic addition reaction.
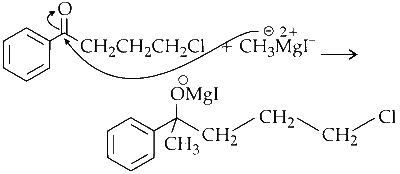
Nucleophilic Substitution :
The highly nucleophilic oxygen attacks the C_1 carbon of the alkyl chain from the back, displacing chlorine to form the final product.
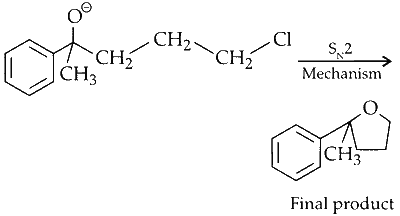
Option (B) in Column I matches with (P) and (S) in Column II.
(C)
Nucleophilic Addition :
The compound undergoes a nucleophilic addition reaction in the presence of $\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4$.
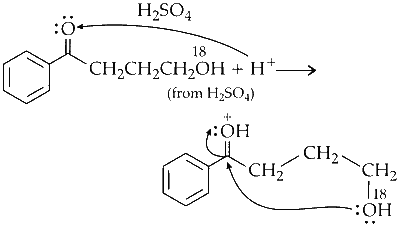
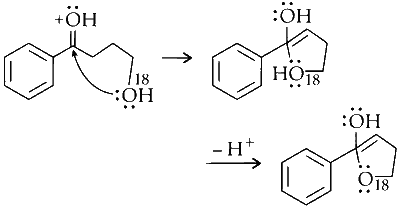
Dehydration :
The molecule loses water, forming an alkene.
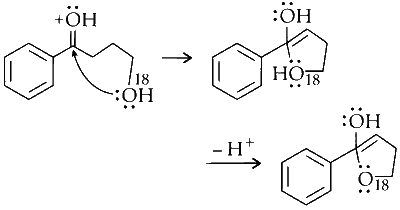
Option (C) in Column I matches with (R) and (S) in Column II.
(D)
The compound reacts with sulfuric acid to form a carbocation, which undergoes electrophilic substitution.
Reaction :
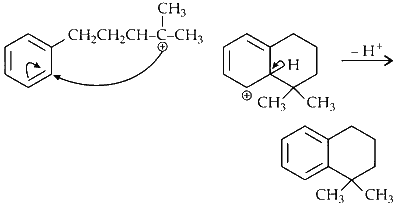
Option (D) in Column I matches with (Q) and (R) in Column II.
Comments (0)


