JEE Advance - Chemistry (2011 - Paper 2 Offline - No. 16)
The total number of contributing structure showing hyper-conjugation (involving C-H bonds) for the following carbocation is _________.
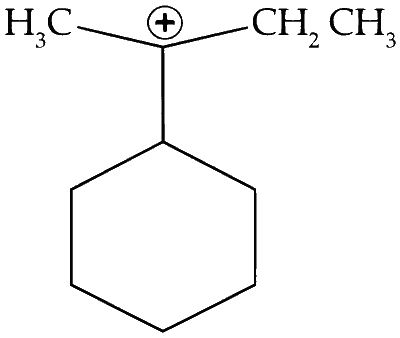
Explanation
(i) Hyper conjugation involves the electrons of $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}$ sigma ( $\sigma$ ) bond, of alkyl group is delocalised with an atom containing empty $p$-orbital (i.e., a carbocation) or unsaturated system.
(ii) For the given carbocation, hypercojugation involves the delocalisation of $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}$ sigma ( $\sigma$ ) bond, of alkyl group with the adjacent atom containing unshared $p$-orbital.
(iii) The different kinds of hydrogen that will be involved in hyperconjugation are as follows :
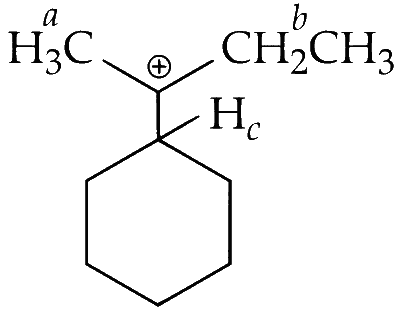
There are three different kinds of hydrogen; $\mathrm{H}_{a^{\prime}} \mathrm{H}_b$ and $\mathrm{H}_c$.
(iv) Hyperconjugative structure due to different kind of hydrogens are as follows :
(a) Hyperconjugation due to $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}_a$ sigma (or $\sigma)$ bond.
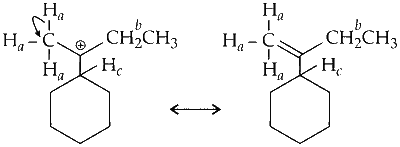
Similarly, two more hyperconjugative structures are possible due to two other hydrogen atoms.
A total of three hyperconjugative structures of carbocation are possible due to delocalisation of $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}_a$ ( $\sigma$ bond) with empty $p$-orbital (on carbocation).
(b) Hyperconjugation due to $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}_b$ sigma (or $\sigma)$ bond.
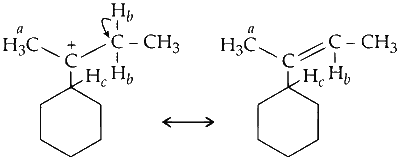
Similarly, one more hyperconjugative structure is possible due to other hydrogen $\left(\mathrm{H}_b\right)$. A total of two hyperconjugative structures of carbocations are possible due to delocalisation of $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}_b$ ( $\sigma$ bond) with empty $p$-orbital (on carbocation).
(c) Hyperconjugation due to $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}_c$ sigma (or $\sigma)$ bond.
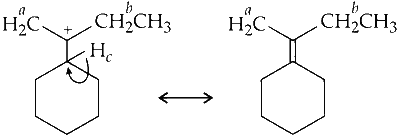
There is only one $\mathrm{H}^c$ hydrogen; hence, one hyperconjugative structure is possible due to delocalisation of $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}_c$ ( $\sigma$ bond) with empty $p$-orbital (on carbocation).
Comments (0)


