JEE Advance - Chemistry (2011 - Paper 1 Offline - No. 23)
Explanation
(i) A decapeptide has nine peptide bonds which hydrolyzes to give ten amino acids. Each peptide bond hydrolyses, to form one molecule of water. Hence, nine molecules of water are required to hydrolysis nine peptide bonds.
$$\text{Decapeptide} \xrightarrow{\text{hydrolyse} +9\, \text{H}_2\text{O}} \text{Amino acids}$$
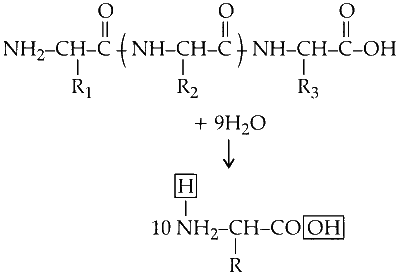
(ii) On hydrolysis a molecule of water (equivalent to 18 g) is added across each amino acid.
Mass of hydrolysed decapeptide = Mass of decapeptide + 9 \times \text{mass of each water molecule}
$= 796 \, \text{g mol}^{-1} + 9 \times 18 \, \text{g mol}^{-1} $
$= (796 + 162) \, \text{g mol}^{-1} $
$= 958 \, \text{g mol}^{-1} $
Mass of glycine in hydrolysed decapeptide
$= \frac{47}{100} \times 958 \, \text{g mol}^{-1} $
$= 450.26 \, \text{g mol}^{-1} $
Mass of each glycine = 75 $\, \text{g mol}^{-1}$
Number of glycine units
$= \frac{\text{Mass of hydrolysed decapeptide}}{\text{Mass of each glycine}} $
$n = \frac{450.26 \, \text{g mol}^{-1}}{75 \, \text{g mol}^{-1}} $
$n = 6.00$
Hence, there are six molecules of water in decapeptide.
Comments (0)


