JEE Advance - Chemistry (2010 - Paper 2 Offline - No. 19)
All the compounds listed in Column I react with water. Match the result of the respective reactions with the appropriate options listed in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
|---|---|
| (A) (CH3)2SiCl2 | (P) Hydrogen halide formation |
| (B) XeF4 | (Q) Redox reaction |
| (C) Cl2 | (R) Reacts with glass |
| (D) VCl5 | (S) Polymerisation |
| (T) O2 formation |
Explanation
(A) Dimethyl silyl chloride undergoes hydration followed by polymerisation owing to the loss of water molecule.
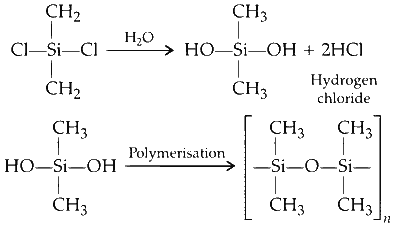
(A) → P, S
$$ \begin{aligned} & \text { (B) } 6 \mathrm{XeF}_4+12 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow 4 \mathrm{Xe}+2 \mathrm{XeO}_3 +24 \mathrm{HF} \text { (Hydrogen fluoride) }+3 \mathrm{O}_2 \text { (Oxygen) } \\ & \end{aligned} $$
Here, xenon undergoes disproportionation reaction (which is a kind of redox reaction) with xenon (in +4 oxidation state) gets oxidized to xenon trioxide $\left(\mathrm{XeO}_3\right)$ and reduced to xenon (Xe) at the same time.
HF reacts with glass as shown :
$$ \mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{SiO}_3+6 \mathrm{HF} \rightarrow \mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{SiF}_6+3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} $$
(B) → P, Q, R, T
(C)
$2 \mathrm{Cl}_2+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow {4 \mathrm{HCl} \text { (Hydrogen } \text { halide )}+\mathrm{O}_2}$
(C) $\rightarrow$ P, Q
(D) $\mathrm{VCl}_5+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow \mathrm{VOCl}_3+2 \mathrm{HCl}$ (Hydrogen chloride)
(D) $\rightarrow P$
Comments (0)


