JEE Advance - Chemistry (2008 - Paper 2 Offline - No. 3)
Explanation
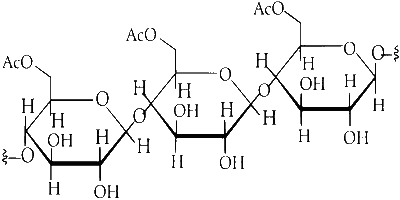
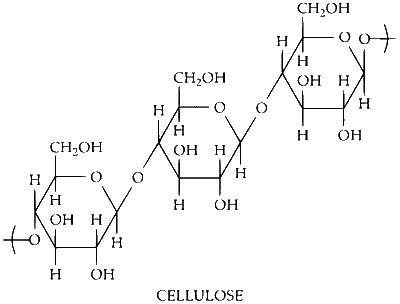
Cellulose is linear chains of $$\beta$$-D-glucose molecules linked together by $$\beta$$-1, 4 glycosidic bonds. Cellulose has $$\beta$$-1, 4 linkage between $$\beta$$-D-glucose units. The cellulose is linear molecule.
A general reaction of alcohol with acetic anhydride is :
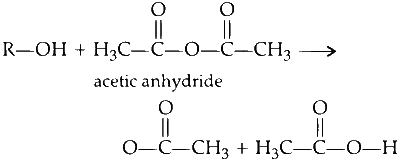
Acetic anhydride reacts with the alcoholic function group and converts the alcoholic function group into ester functional group. The $$-$$OH is known as an alcoholic functional group. The $$-$$OC(O)$$-$$ is known as an ester functional group.
During the conversion hydrogen of alcoholic group is replaced by CH$$_3$$CO$$-$$ group of acetic anhydride. The above reaction is known as acetylation because acetyl group CH$$_3$$CO$$-$$ is attaching with the reactant alcohol.
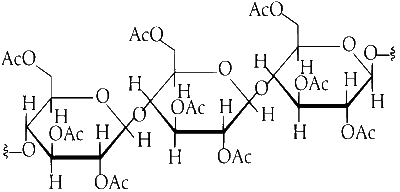
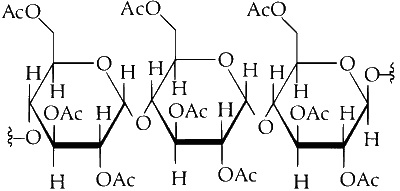
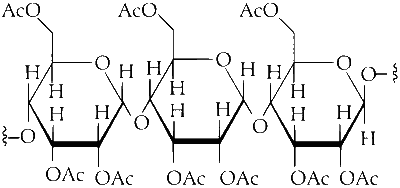
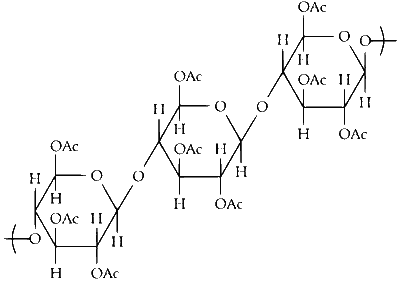
So, upon acetylation of cellulose with excess acetic anhydride/H$$_2$$SO$$_4$$ (catalytic) all the $$-$$OH group will convert into acetyl group.
As the cellulose contains a large number of glucose units but our product is triacetate. It means the alcohol group of three glucose units of cellulose is converted into acetyl group. As the acetic anhydride is in excess, all alcoholic groups of three glucose units of cellulose will convert into acetyl groups.
So, the structure of the product is
Comments (0)


