JEE Advance - Chemistry (2008 - Paper 1 Offline - No. 7)
Explanation
Weak monoacidic base, e.g., BOH is neutralised as follows:
BOH + HCl $$\to$$ BCl + H$$_2$$O
At the equivalence point, all BOH get converted into the salt. The concentration of H$$^+$$ (or pH of solution) is due to hydrolysis of the resultant salt (BCl, cationic hydrolysis here.)
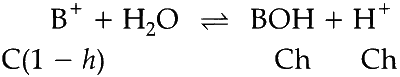
Volume of HCl used up,
$${V_a} = {{{N_b}{V_b}} \over {{N_a}}}$$
$${V_a} = {{2.5 \times 2 \times 15} \over {2 \times 5}}$$
$${V_a} = 7.5$$
Concentration of salt,
$$[BCl] = {{conc.\,of\,base} \over {total\,volume}}$$
$$ = {{2 \times 2.5} \over {5(7.5 + 2.5)}} = {1 \over {10}} = 0.1$$
$${K_h} = {{C{h^2}} \over {1 - h}} = {{{K_w}} \over {{K_b}}} = {{{{10}^{ - 14}}} \over {{{10}^{ - 12}}}}$$
$$ = {10^{ - 2}} = {{0.1 \times {h^2}} \over {1 - h}}$$ ..... (i)
(h should be estimated whether that can be neglected or not.)
On calculating, $$h = 0.27$$ (significant, not negligible)
$$[{H^ + }] = Ch = 0.1 \times 0.27 = 2.7 \times {10^{ - 2}}$$ M
Comments (0)


