JEE Advance - Chemistry (1986 - No. 23)
CH3CH2CH = CHCOOH
Explanation
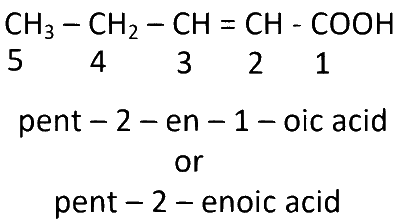
Note :
(1) Here functional group $$-$$COOH present. All functional groups add as secondary suffix.
(a) If carbon atom of $$-$$COOH group present in main chain then secondary suffix name is $$\to$$ oic acid.
(b) If carbon atom of $$-$$COOH group present not in main chain then secondary suffix name is $$\to$$ carboxylic acid.
As here carbon atom of $$-$$COOH group present in main chain that is why we use oic acid.
(2) Functional group should always get lowest possible number.
(3) Alkane, alkene(=) and alkyne($$\equiv$$) always act as primary suffix.
For alkane we use word "ane".
For alkene we use word "ene".
For alkyne we use word "yne".
Here alkene(=) present so we use word "ene" as primary suffix.
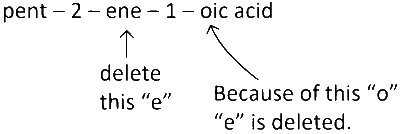
(4) After last e of "ene" if we get a, i, o, u, y as the first letter of secondary suffix then we delete e.
Here in the name $$\to$$
(5) Naming is done by following way $$\to$$
Prefix + word root + suffix(p) + suffix(s)
(a) Here no prefix (name of side chain) as there is no side chain present.
(b) Word root represent number of carbon atom in main chain.
Here in main chain 5 carbon atoms present so word root is "pent".
(c) Primary suffix is alkene.
(d) Secondary suffix is function group $$-$$COOH. It's name oic acid.
(6) If functional group's carbon get number "1" then we can ignore it in nomenclature. So it's nomenclature can be also $$\to$$
$$\mathrm{pent - 2 - enoic\,acid}$$
Comments (0)


