JEE MAIN - Physics (2010 - No. 7)
A rectangular loop has a sliding connector $$PQ$$ of length $$l$$ and resistance $$R$$ $$\Omega $$ and it is moving with a speed $$v$$ as shown. The set-up is placed in a uniform magnetic field going into the plane of the paper. The three currents $${I_1},{I_2}$$ and $$I$$ are
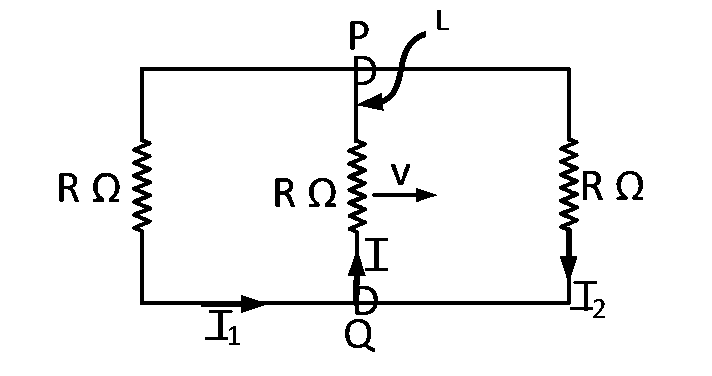

$${I_1} = - {I_2} = {{Blv} \over {6R}},\,\,I = {{2Blv} \over {6R}}$$
$${I_1} = {I_2} = {{Blv} \over {3R}},\,\,I = {{2Blv} \over {3R}}$$
$${I_1} = {I_2} = I = {{Blv} \over R}$$
$${I_1} = {I_2} = {{Blv} \over {6R}},I = {{Blv} \over {3R}}$$
Explanation
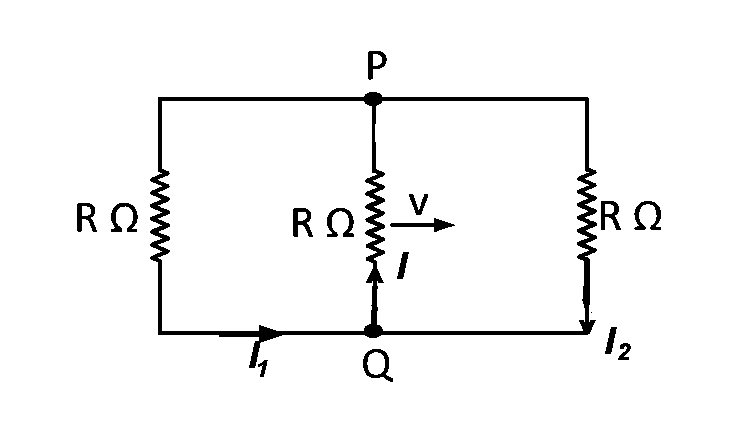
Due to the movement of resistor $$R,$$ an $$emf$$ equal to $$Blv$$ will be induced in it as shown in figure clearly,
$$I = {I_1} + {I_2}$$
<
Also, $${I_1} = {I_2}$$
Solving the circuit, we get
$${I_1} = {I_2} = {{Blv} \over {3R}}$$
and $$I = 2{I_1} = {{2Blv} \over {3R}}$$
Comments (0)


