JEE MAIN - Physics (2004 - No. 15)
An electric current is passed through a circuit containing two wires of the same material, connected in parallel. If the lengths and radii are in the ratio of $${4 \over 3}$$ and $${2 \over 3}$$, then the ratio of the current passing through the wires will be
$$8/9$$
$$1/3$$
$$3$$
$$2$$
Explanation
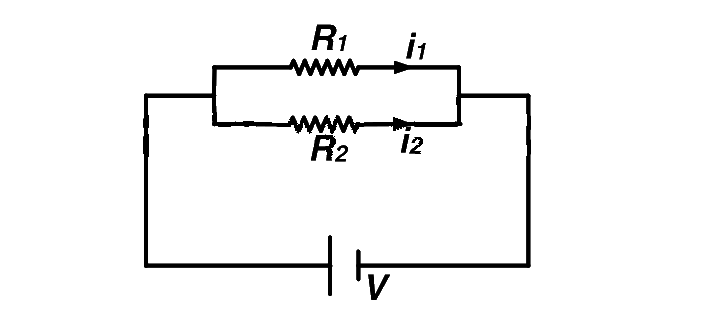
$${i_1}{R_1} = {i_2}{R_2}\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,$$ (same potential difference)
V = I1R1 = I1$$ \times $$$${{\rho {l_1}} \over {\pi r_1^2}}$$
Also V = I2R2 = I2$$ \times $$$${{\rho {l_2}} \over {\pi r_2^2}}$$
$$ \therefore $$ I1$$ \times $$$${{\rho {l_1}} \over {\pi r_1^2}}$$ = I2$$ \times $$$${{\rho {l_2}} \over {\pi r_2^2}}$$
$$ \Rightarrow $$ $${{{I_1}} \over {{I_2}}} = {{{\ell _1}} \over {{\ell _2}}} \times {{r_1^2} \over {r_2^2}}$$
$$ = {3 \over 4} \times {4 \over 9} = {1 \over 3}\,\,$$
Comments (0)


