JEE MAIN - Mathematics (2005 - No. 48)
If the pair of lines $$a{x^2} + 2\left( {a + b} \right)xy + b{y^2} = 0$$ lie along diameters of a circle and divide the circle into four sectors such that the area of one of the sectors is thrice the area of another sector then :
$$3{a^2} - 10ab + 3{b^2} = 0$$
$$3{a^2} - 2ab + 3{b^2} = 0$$
$$3{a^2} + 10ab + 3{b^2} = 0$$
$$3{a^2} + 2ab + 3{b^2} = 0$$
Explanation
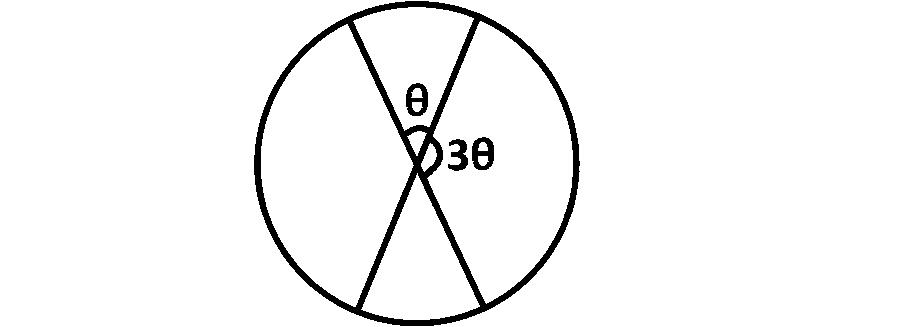
As per question area of one sector $$=3$$ area of another sector
$$ \Rightarrow $$ at center by one sector $$ = 3 \times $$ angle at center by another sector
Let one angle be $$\theta $$ then other $$=30$$
Clearly $$\theta + 3\theta = 180 \Rightarrow \theta = {45^ \circ }$$
$$\therefore$$ Angle between the diameters represented by combined equation
$$a{x^2} + 2\left( {a + b\,\,\,xy} \right) + b{y^2} = 0$$ is $${45^ \circ }$$
$$\therefore$$ Using $$tan$$ $$\theta $$ $$ = {{2\sqrt {{h^2} - ab} } \over {a + b}}$$
we get $$\tan \,{45^ \circ } = {{2\sqrt {{{\left( {a + b} \right)}^2} - ab} } \over {a + b}}$$
$$ \Rightarrow 1 = {{2\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2} + ab} } \over {a + b}}$$
$$ \Rightarrow {\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = 4\left( {{a^2} + {b^2} + ab} \right)$$
$$ \Rightarrow {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab = 4{a^2} + 4{b^2} + 4ab$$
$$ \Rightarrow 3{a^2} + 3{b^2} + 2ab = 0$$
Comments (0)


