JEE MAIN - Mathematics (2005 - No. 21)
The area enclosed between the curve $$y = {\log _e}\left( {x + e} \right)$$ and the coordinate axes is :
$$1$$
$$2$$
$$3$$
$$4$$
Explanation
The graph of the curve $$y = {\log _e}\left( {x + e} \right)$$ is as shown in the fig.
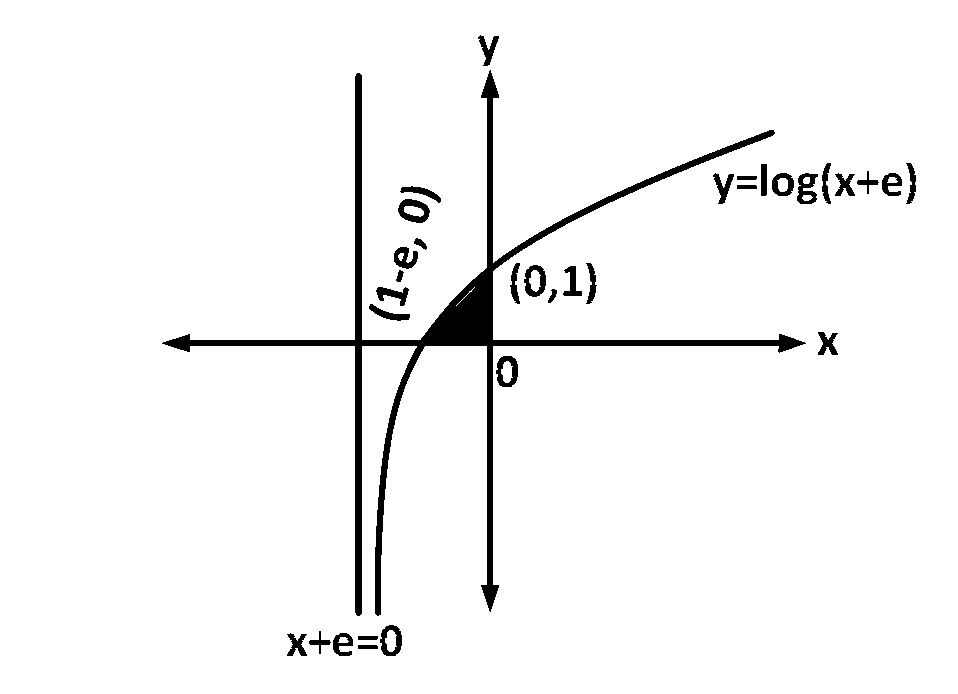
Required area
$$A = \int\limits_{1 - e}^0 {ydx} = \int\limits_{1 - e}^0 {{{\log }_e}} \left( {x + e} \right)dx$$
put $$x + e = t \Rightarrow dx = dt$$
also At $$x = 1 - e,t = 1$$
At $$x = 0,\,\,t = e$$
$$\therefore$$ $$A = \int\limits_1^e {{{\log }_e}} \,tdt = \left[ {t\,{{\log }_e}t - t_1^e} \right]$$
$$e - e - 0 + 1 = 1$$
Hence the required area is $$1$$ square unit.

Required area
$$A = \int\limits_{1 - e}^0 {ydx} = \int\limits_{1 - e}^0 {{{\log }_e}} \left( {x + e} \right)dx$$
put $$x + e = t \Rightarrow dx = dt$$
also At $$x = 1 - e,t = 1$$
At $$x = 0,\,\,t = e$$
$$\therefore$$ $$A = \int\limits_1^e {{{\log }_e}} \,tdt = \left[ {t\,{{\log }_e}t - t_1^e} \right]$$
$$e - e - 0 + 1 = 1$$
Hence the required area is $$1$$ square unit.
Comments (0)


