JEE MAIN - Mathematics (2002 - No. 22)
The equation of a circle with origin as a center and passing through an equilateral triangle whose median is of length $$3$$$$a$$ is :
$${x^2}\, + \,{y^2} = 9{a^2}$$
$${x^2}\, + \,{y^2} = 16{a^2}$$
$${x^2}\, + \,{y^2} = 4{a^2}$$
$${x^2}\, + \,{y^2} = {a^2}$$
Explanation
Let $$ABC$$ be an equilateral triangle, whose median is $$AD.$$
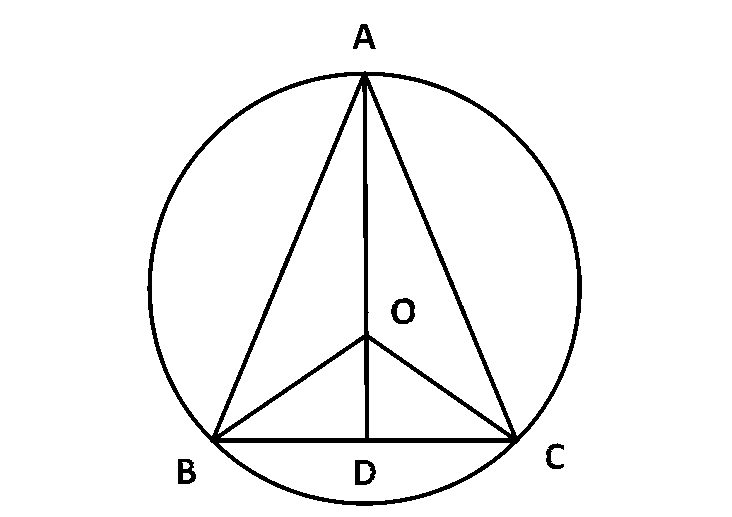
Given $$AD=3a.$$
In $$\Delta ABD,\,\,A{B^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2};$$
$$ \Rightarrow {x^2} = 9{a^2} + \left( {{x^2}/4} \right)\,\,$$
where $$AB = BC = AC = x.$$
$${3 \over 4}{x^2} = 9{a^2} \Rightarrow {x^2} = 12{a^2}.$$
In $$\,\,\,\Delta OBD,O{B^2} = O{D^2} + B{D^2}$$
$$ \Rightarrow {r^2} = {\left( {3a - r} \right)^2} + {{{x^2}} \over 4}$$
$$ \Rightarrow {r^2} = 9{a^2} - 6ar + {r^2} + 3{a^2};$$
$$ \Rightarrow 6ar = 12{a^2}$$
$$ \Rightarrow r = 2a$$
So equation of circle is $${x^2} + {y^2} = 4{a^2}$$

Given $$AD=3a.$$
In $$\Delta ABD,\,\,A{B^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2};$$
$$ \Rightarrow {x^2} = 9{a^2} + \left( {{x^2}/4} \right)\,\,$$
where $$AB = BC = AC = x.$$
$${3 \over 4}{x^2} = 9{a^2} \Rightarrow {x^2} = 12{a^2}.$$
In $$\,\,\,\Delta OBD,O{B^2} = O{D^2} + B{D^2}$$
$$ \Rightarrow {r^2} = {\left( {3a - r} \right)^2} + {{{x^2}} \over 4}$$
$$ \Rightarrow {r^2} = 9{a^2} - 6ar + {r^2} + 3{a^2};$$
$$ \Rightarrow 6ar = 12{a^2}$$
$$ \Rightarrow r = 2a$$
So equation of circle is $${x^2} + {y^2} = 4{a^2}$$
Comments (0)


