JEE MAIN - Chemistry (2002 - No. 61)
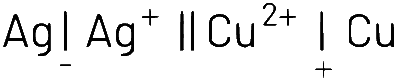
$$ \begin{aligned} \mathrm{Ag}^{+}+\mathrm{e}^{-} & \longrightarrow \mathrm{Ag}; E^{\circ}=x \\\\ \mathrm{Cu}^{2+}+2 e^{-} & \longrightarrow \mathrm{Cu}{;} E^{\circ}=y \end{aligned} $$
$$ E^{\circ} \text { cell is } $$ :
Explanation
The cell notation indicates that the left side (Ag|Ag+) is the anode (oxidation occurs), and the right side (Cu²⁺|Cu) is the cathode (reduction occurs). In a galvanic (voltaic) cell, electrons flow from anode to cathode.
The standard cell potential (E° cell) is the difference in potential between the cathode and anode. It's calculated as :
E°cell = E°cathode - E°anode
At LHS (oxidation) :
$$
2 \times\left(\mathrm{Ag} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Ag}^{+}+\mathrm{e}^{-}\right); \quad E_{\text {oxi }}^{\circ}=-x
$$
At RHS (reduction) :
$$
\mathrm{Cu}^{2+}+2 e^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Cu}; \quad \mathrm{E}_{\text {red }}^{\circ}=+y
$$
$$
2 \mathrm{Ag}+\mathrm{Cu}^{2+} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Cu}+2 \mathrm{Ag}^{+}, E_{\text {cell }}^{\circ}=(y-x)
$$
_____________________________________________________
$$ \therefore $$ E°cell = y - x
Therefore, the correct answer is :
Option C : y - x.
Comments (0)


