JAMB - Physics (2001 - No. 45)
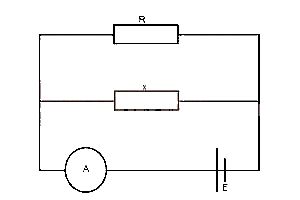
In the circuit diagram above , the ammeter reads a current of 3A when R is 5Ω and 6A when R is 2Ω. Determine the value of x
8Ω
2Ω
10Ω
4Ω
Explanation
for a parallel R and X, when R = 5Ω,
Effective resistance R = \(\frac{5X}{5 + X}\)
and when R = 2Ω
Effective resistance R = \(\frac{2X}{2 + X}\)
Thus since E = I(R+r), and if r = 0 then E = IR
∴(i) E = 3(\(\frac{5X}{(5+x)}\)); (ii) E = 6(\(\frac{2X}{(2+x)}\))
∴3(\(\frac{5X}{(5+X)}\)) = 6(\(\frac{2X}{(2+X)}\))
=> (\(\frac{5X}{(5+X)}\)) = 2(\(\frac{2x}{(2+X)}\))
∴ (\(\frac{5X}{(5+X)}\)) = (\(\frac{4X}{(2+X)}\))
5x(2+x) = 4x(5+x)
10x + 5x\(^2\) = 20x + 4x\(^2\)
5x\(^2\) - 4x\(^2\) = 20x - 10x
=> x\(^2\) = 10x
∴x\(^2\) - 10x = 0
x(x - 10) = 0
∴ x = 0 or 10
∴ x = 10Ω
Comments (0)


