JAMB - Biology (2007 - No. 33)
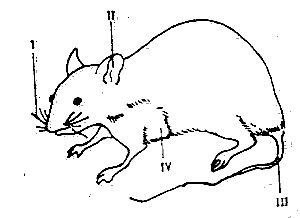
Use the diagram above to answer this question. The type of protective adaptation exhibited by the animal is
Explanation
The correct answer is C. Countershading colouration.
African rats often have a darker color on their backs (dorsal side) and a lighter color on their bellies (ventral side). This coloration pattern is an example of countershading, which helps to:
- Reduce visibility by breaking up the outline of the body
- Create a sense of volume and depth, making it harder for predators to detect the rat's shape and movement. Countershading is a type of protective coloration that helps animals blend in with their surroundings and avoid detection.
The other options are not the best fit:
A. Disruptive colouration involves bold, contrasting patterns that break up an animal's outline, making it harder to see. While African rats may have some disruptive patterns, countershading is a more accurate description.
B. Flash colouration refers to bright, striking colours used for communication, mating, or warning. African rats do not typically exhibit flash colouration.
D. Warning colouration involves bright, conspicuous colors that signal to predators that an animal is toxic, distasteful, or otherwise unpalatable. African rats do not typically exhibit warning colouration.
Comments (0)


